PNPLA3 I148M mediates the regulatory effect of NF-kB on inflammation in PA-treated HepG2 cells
- PMID: 31793207
- PMCID: PMC6991629
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.14839
PNPLA3 I148M mediates the regulatory effect of NF-kB on inflammation in PA-treated HepG2 cells
Abstract
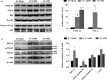
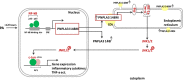
Both PNPLA3 I148M and hepatic inflammation are associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) progression. This study aimed to elucidate whether PNPLA3 I148M is involved in NF-kB-related inflammation regulation in NAFLD. HepG2 cells homozygous for the PNPLA3 I148M mutation were used. The human PNPLA3 promoter sequence was screened for NF-kB binding sites using the MATCH and PATCH tools. NF-kB-mediated transcriptional regulation of the PNPLA3 gene was assessed by luciferase reporter assay, EMSA and ChIP-qPCR. Wild-type (I148I) and mutant (M148M) PNPLA3 were overexpressed using stable lentivirus-mediated transfection. The pCMV vector and siRNA were transiently transfected into cells to direct NF-kB overexpression and PNPLA3 silencing, respectively. A putative NF-kB binding site in the human PNPLA3 promoter was shown to be necessary for basal and NF-kB-driven transcriptional activation of PNPLA3 and protein/DNA complex formation. Supershift analysis demonstrated a protein/DNA complex specifically containing the NF-kB p65 and p50 subunits. ChIP-qPCR confirmed the endogenous binding of NF-kB to the human PNPLA3 promoter in response to NF-kB overexpression and palmitic acid (PA) challenge. The silencing of PNPLA3 blocked the overexpression of NF-kB or PA-induced TNF-α up-regulation. Moreover, mutant PNPLA3 overexpression prevented NF-kB inhibitor-induced down-regulation of TNF-α expression in PA-treated HepG2 cells. Finally, the overexpression of mutant but not wild-type PNPLA3 increased TNF-α expression and activated the ER stress-mediated and NF-kB-independent inflammatory IRE-1α/JNK/c-Jun pathway. Human PNPLA3 was shown to be a target of NF-kB, and PNPLA3 I148M mediated the regulatory effect of NF-kB on inflammation in PA-treated HepG2 cells, most likely via the IRE-1α/JNK/c-Jun ER stress pathway.
Keywords: ER stress; NAFLD; NF-kB; PNPLA3; inflammation.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[The influence of patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 on palmitic acid-induced hepatocyte apoptosis].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016 May 24;96(19):1535-9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2016.19.016. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27266503 Chinese.
-
Identification of a Metabolic, Transcriptomic, and Molecular Signature of Patatin-Like Phospholipase Domain Containing 3-Mediated Acceleration of Steatohepatitis.Hepatology. 2021 Apr;73(4):1290-1306. doi: 10.1002/hep.31609. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Hepatology. 2021. PMID: 33131062 Free PMC article.
-
PNPLA3 I148M is involved in the variability in anti-NAFLD response to exenatide.Endocrine. 2020 Dec;70(3):517-525. doi: 10.1007/s12020-020-02470-7. Epub 2020 Aug 30. Endocrine. 2020. PMID: 32862405
-
PNPLA3 I148M variant in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: demographic and ethnic characteristics and the role of the variant in nonalcoholic fatty liver fibrosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jan 21;21(3):794-802. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.794. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25624712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RUNX1: A Regulator of NF-kB Signaling in Pulmonary Diseases.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2018;19(2):172-178. doi: 10.2174/1389203718666171009111835. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2018. PMID: 28990531 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial Mutations and Genetic Factors Determining NAFLD Risk.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 24;22(9):4459. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094459. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33923295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PNPLA3 148M/M Is More Susceptible to Palmitic Acid-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Associated Apoptosis in HepG2 Cells.Int J Endocrinol. 2023 Feb 14;2023:2872408. doi: 10.1155/2023/2872408. eCollection 2023. Int J Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 36825197 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in genetic variation in metabolism-related fatty liver disease.Front Genet. 2023 Sep 11;14:1213916. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1213916. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37753315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
α‑rhamnrtin‑3‑α‑rhamnoside exerts anti‑inflammatory effects on lipopolysaccharide‑stimulated RAW264.7 cells by abrogating NF‑κB and activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Nov;24(5):799. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12439. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34523697 Free PMC article.
-
Doxepin Exacerbates Renal Damage, Glucose Intolerance, Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, and Urinary Chromium Loss in Obese Mice.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Mar 16;14(3):267. doi: 10.3390/ph14030267. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33809508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zeng MD, Fan JG, Lu LG, et al. Chinese national consensus workshop on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases. J Dig Dis. 2008;9:108‐112. - PubMed
-
- Lewis JR, Mohanty SR. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a review and update. Dig Dis Sci. 2010;55:560‐578. - PubMed
-
- Mishra P, Younossi ZM. Current treatment strategies for non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2007;4:133‐140. - PubMed
-
- Pingitore P, Pirazzi C, Mancina RM, et al. Recombinant PNPLA3 protein shows triglyceride hydrolase activity and its I148M mutation results in loss of function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1841:574‐580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

