Platyconic Acid A, Platycodi Radix-Derived Saponin, Suppresses TGF-1-induced Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells via Blocking SMAD and Activating the PPAR Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 31795488
- PMCID: PMC6952772
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8121544
Platyconic Acid A, Platycodi Radix-Derived Saponin, Suppresses TGF-1-induced Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells via Blocking SMAD and Activating the PPAR Signaling Pathway
Abstract
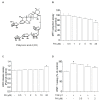
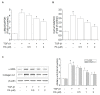
Platycodi radix is a widely sold health food worldwide, which contains numerous phytochemicals that are beneficial to health. Previously, we reported that saponin from the roots of Platycodi radix-derived saponin inhibited toxicant-induced liver diseases. Nevertheless, the inhibitory effect of platyconic acid A (PA), the active component of Platycodi radix-derived saponin, on the anti-fibrotic activity involving the SMAD pathway remains unclear. We investigated the inhibitory effects of PA on TGF-1-induced activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). PA inhibited TGF-1-enhanced cell proliferation, as well as expression of -SMA and collagen 1 in HSC-T6 cells. PA suppressed TGF-1-induced smad2/3 phosphorylation and smad binding elements 4 (SBE4) luciferase activity. Reversely, PA restored TGF-1-reduced expression of smad7 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)γ. PA also repressed TGF-1-induced phosphorylation of Akt and MAPKs. In summary, the results suggest that the inhibitory effect of PA on HSCs occurs through the blocking of SMAD-dependent and SMAD-independent pathways, leading to the suppression of -SMA and collagen 1 expression.
Keywords: PPARγ; SMAD; TGF-1; hepatic stellate cells; platyconic acid A.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activity affects the hepatic stellate cell activation and the progression of NASH via TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway.J Physiol Biochem. 2021 Feb;77(1):35-45. doi: 10.1007/s13105-020-00777-7. Epub 2020 Nov 14. J Physiol Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33188625
-
Astragalus and Paeoniae Radix Rubra extract (APE) inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation by modulating transforming growth factor-β/Smad pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Apr;11(4):2569-77. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.3026. Epub 2014 Dec 1. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25435153 Free PMC article.
-
Capsaicin Inhibits Dimethylnitrosamine-Induced Hepatic Fibrosis by Inhibiting the TGF-β1/Smad Pathway via Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Activation.J Agric Food Chem. 2017 Jan 18;65(2):317-326. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b04805. Epub 2017 Jan 3. J Agric Food Chem. 2017. PMID: 27991776
-
Compound Astragalus and Salvia miltiorrhiza extracts modulate MAPK-regulated TGF-β/Smad signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma by multi-target mechanism.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Jul 1;169:219-28. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.04.013. Epub 2015 Apr 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25934513
-
Saponin as regulator of biofuel: implication for ethnobotanical management of diabetes.J Physiol Biochem. 2014 Jun;70(2):555-67. doi: 10.1007/s13105-014-0325-4. Epub 2014 Feb 25. J Physiol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24563096 Review.
Cited by
-
PPAR-Mediated Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology.Cells. 2020 Feb 3;9(2):352. doi: 10.3390/cells9020352. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32028670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P4HB regulates the TGFβ/SMAD3 signaling pathway through PRMT1 to participate in high glucose-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and fibrosis of renal tubular epithelial cells.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Sep 9;25(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03733-5. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39251943 Free PMC article.
-
Platyconic acid A‑induced PPM1A upregulation inhibits the proliferation, inflammation and extracellular matrix deposition of TGF‑β1‑induced lung fibroblasts.Mol Med Rep. 2022 Nov;26(5):329. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12845. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 36069235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neuman M.G., French S.W., Zakhari S., Malnick S., Seitz H.K., Cohen L.B., Salaspuro M., Voinea-Griffin A., Barasch A., Kirpich I.A., et al. Alcohol, microbiome, life style influence alcohol and non-alcoholic organ damage. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2017;102:162–180. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2017.01.003. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

