Does a tailored intervention to promote adherence in patients with chronic lung disease affect exacerbations? A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 31796013
- PMCID: PMC6892023
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-019-1219-3
Does a tailored intervention to promote adherence in patients with chronic lung disease affect exacerbations? A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Poor medication-adherence is common in chronic lung patients, resulting in reduced health-outcomes and increased healthcare-costs. This study aimed to investigate the impact of an acoustic reminder and support calls on adherence to inhaled therapy in asthma and COPD patients and to determine their effect on exacerbations.
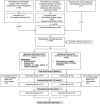
Methods: This single-blinded randomized controlled trial investigated asthma and COPD patients during 6 months in an ambulatory setting. The intervention consisted of daily alarm clock and support phone calls, whenever use of rescue medication doubled or inhaled medication was not taken as prescribed. Primary outcome was time to next exacerbation. Frequency of exacerbations, adherence to inhaled medication and quality of life scores were secondary outcomes. Cox and Poisson regression were used to determine intervention effect on time to exacerbation and frequency of exacerbations, respectively.
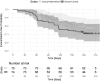
Results: Seventy-five participants were assigned to the intervention group and 74 to usual follow-up care. During a median follow-up of 6.2 months, 22 and 28% in the intervention and control groups respectively, experienced at least one exacerbation. Intervention had no effect on time to first exacerbation (HR 0.65, 95% CI 0.21 to 2.07, P = .24), but showed a trend toward a 39% decreased frequency of exacerbations (RR = 0.61, 95% CI 0.35 to 1.03, P = .070) for the adjusted models, respectively. The intervention group had significantly more days with 80-100% taking adherence regarding puff inhalers (82 ± 14% vs. 60 ± 30%, P < .001) and dry powder capsules (90 ± .10% vs. 80 ± 21%, P = .01). Timing adherence in participants using puff inhalers was higher in the intervention group (69 ± 25% vs. 51 ± 33%, P < .001). No significant differences in QoL were found between the two groups.
Conclusion: Participants assigned to the intervention group had significantly better taking and timing adherence of inhaled medication resulting in a trend towards a decreased frequency of exacerbations. However, no effect on time to next exacerbation was observed.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT02386722, Registered 14 February 2014.
Keywords: Chronic disease management; Compliance; Randomised controlled trial; Reminders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Use and inhalation technique of inhaled medication in patients with asthma and COPD: data from a randomized controlled trial.Respir Res. 2018 Dec 3;19(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s12931-018-0936-3. Respir Res. 2018. PMID: 30509268 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of an Electronic Monitoring Intervention to Improve Adherence to Inhaled Medication in Patients with Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial.JMIR Res Protoc. 2017 Oct 23;6(10):e204. doi: 10.2196/resprot.7522. JMIR Res Protoc. 2017. PMID: 29061556 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of an electronic monitoring device with audiovisual reminder function on adherence to inhaled corticosteroids and school attendance in children with asthma: a randomised controlled trial.Lancet Respir Med. 2015 Mar;3(3):210-9. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(15)00008-9. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Lancet Respir Med. 2015. PMID: 25617215 Clinical Trial.
-
Tiotropium bromide. A review of its use as maintenance therapy in patients with COPD.Treat Respir Med. 2004;3(4):247-68. doi: 10.2165/00151829-200403040-00005. Treat Respir Med. 2004. PMID: 15350163 Review.
-
Effect of corticosteroids on exacerbations of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2004;1(3):161-6. doi: 10.1513/pats.200402-008MS. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2004. PMID: 16113429 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of health education intervention on treatment adherence and health status in patients with Chronic obstruction pulmonary disease: A random control trial.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 24;20(6):e0325192. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325192. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40554530 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Advancing Digital Solutions to Overcome Longstanding Barriers in Asthma and COPD Management.Patient Prefer Adherence. 2023 Jan 28;17:259-272. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S385857. eCollection 2023. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2023. PMID: 36741814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Digital Inhalers for Asthma or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Scientific Perspective.Pulm Ther. 2021 Dec;7(2):345-376. doi: 10.1007/s41030-021-00167-4. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Pulm Ther. 2021. PMID: 34379316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Triple Therapy in COPD in Real Life: Is It Better to Use Single or Multiple Inhalers?J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 17;13(20):6191. doi: 10.3390/jcm13206191. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39458140 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Effectiveness of Umeclidinium/Vilanterol versus Inhaled Corticosteroid/Long-Acting β2-Agonist in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in a Primary Care Setting in England.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023 Apr 19;18:643-659. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S405498. eCollection 2023. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023. PMID: 37155496 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global surveillance, prevention and control of chronic respiratory diseases: a comprehensive approach. 2007.