Low 2018/19 vaccine effectiveness against influenza A(H3N2) among 15-64-year-olds in Europe: exploration by birth cohort
- PMID: 31796152
- PMCID: PMC6891946
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2019.24.48.1900604
Low 2018/19 vaccine effectiveness against influenza A(H3N2) among 15-64-year-olds in Europe: exploration by birth cohort
Abstract
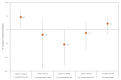
IntroductionInfluenza A(H3N2) clades 3C.2a and 3C.3a co-circulated in Europe in 2018/19. Immunological imprinting by first childhood influenza infection may induce future birth cohort differences in vaccine effectiveness (VE).AimThe I-MOVE multicentre primary care test-negative study assessed 2018/19 influenza A(H3N2) VE by age and genetic subgroups to explore VE by birth cohort.MethodsWe measured VE against influenza A(H3N2) and (sub)clades. We stratified VE by usual age groups (0-14, 15-64, ≥ 65-years). To assess the imprint-regulated effect of vaccine (I-REV) hypothesis, we further stratified the middle-aged group, notably including 32-54-year-olds (1964-86) sharing potential childhood imprinting to serine at haemagglutinin position 159.ResultsInfluenza A(H3N2) VE among all ages was -1% (95% confidence interval (CI): -24 to 18) and 46% (95% CI: 8-68), -26% (95% CI: -66 to 4) and 20% (95% CI: -20 to 46) among 0-14, 15-64 and ≥ 65-year-olds, respectively. Among 15-64-year-olds, VE against clades 3C.2a1b and 3C.3a was 15% (95% CI: -34 to 50) and -74% (95% CI: -259 to 16), respectively. VE was -18% (95% CI: -140 to 41), -53% (95% CI: -131 to -2) and -12% (95% CI: -74 to 28) among 15-31-year-olds (1987-2003), 32-54-year-olds (1964-86) and 55-64-year-olds (1954-63), respectively.DiscussionThe lowest 2018/19 influenza A(H3N2) VE was against clade 3C.3a and among those born 1964-86, corresponding to the I-REV hypothesis. The low influenza A(H3N2) VE in 15-64-year-olds and the public health impact of the I-REV hypothesis warrant further study.
Keywords: A(H3N2); birth cohorts; imprinting; influenza; multicentre study; vaccine effectiveness.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC), World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe (WHO/Europe). Flu News Europe. Summary week 20/2019 (13-20 May 2019). 13-May-2019. Stockholm: ECDC; 2019. Available from: https://flunewseurope.org/Archives/GetFile?fileId=422
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Addendum to the recommended composition of influenza virus vaccines for use in the 2019-2020 northern hemisphere influenza season. Geneva: WHO; 2019. Available from: https://www.who.int/influenza/vaccines/virus/recommendations/201902_reco...
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Recommended composition of influenza virus vaccines for use in the 2018-2019 northern hemisphere influenza season. Geneva: WHO; 2018. Available from: https://www.who.int/influenza/vaccines/virus/recommendations/201802_reco...
-
- Kissling E, Valenciano M, Pozo F, Vilcu AM, Reuss A, Rizzo C, et al. 2015/16 I-MOVE/I-MOVE+ multicentre case-control study in Europe: Moderate vaccine effectiveness estimates against influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 and low estimates against lineage-mismatched influenza B among children. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2018;12(4):423-37. 10.1111/irv.12520 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kissling E, Pozo F, Buda S, Vilcu AM, Rizzo C, Gherasim A, et al. Effectiveness of influenza vaccine against influenza A in Europe in seasons of different A(H1N1)pdm09 and the same A(H3N2) vaccine components (2016-17 and 2017-18). Vaccine X. 2019;3:100042. 10.1016/j.jvacx.2019.100042 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
