Alveolar bone repair of rhesus monkeys by using BMP-2 gene and mesenchymal stem cells loaded three-dimensional printed bioglass scaffold
- PMID: 31796797
- PMCID: PMC6890714
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-54551-x
Alveolar bone repair of rhesus monkeys by using BMP-2 gene and mesenchymal stem cells loaded three-dimensional printed bioglass scaffold
Abstract
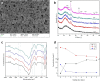
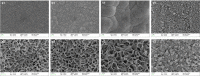
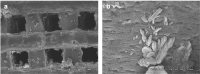
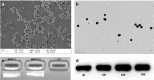
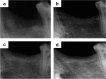
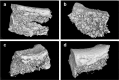
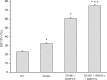
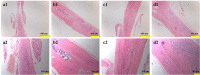
Over the past years, the study about bone tissue engineering in the field of regenerative medicine has been a main research topic. Using three-dimensional (3D) porous degradable scaffold complexed with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and growth factor gene to improve bone tissue repair and regeneration has raised much interest. This study mainly evaluated the osteogenesis of alveolar bone defects of animal in the following experimental groups: sham-operated (SO), 3D printed bioglass (3D-BG), 3D-BG with BMP-2 gene loaded CS (3D-BG + BMP/CS) and 3D-BG with rhesus marrow bone MSCs and BMP/CS (3D-BG + BMP/CS + rBMSCs). Simulated human bone defect with critical size of 10 × 10 × 5 mm were established in quadrumana - rhesus monkeys, and in vivo osteogenesis was characterized by X-ray, micro-Computed Tomography (mCT) and history. Our results revealed that 3D-BG + rBMSCs + BMP/CS scaffold could improve bone healing best by showing its promote osteogenic properties in vivo. Considering the great bone repair capacity of 3D-BG + BMP/CS + rBMSCs in humanoid primate rhesus monkeys, it could be a promising therapeutic strategy for surgery trauma or accidents, especially for alveolar bones defects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
BMP-2 and hMSC dual delivery onto 3D printed PLA-Biogel scaffold for critical-size bone defect regeneration in rabbit tibia.Biomed Mater. 2020 Dec 12;16(1):015019. doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/aba879. Biomed Mater. 2020. PMID: 32698169
-
Evaluation of BMP-2 and VEGF loaded 3D printed hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds with enhanced osteogenic capacity in vitro and in vivo.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020 Jul;112:110893. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.110893. Epub 2020 Mar 21. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020. PMID: 32409051
-
A Novel 3D-bioprinted Porous Nano Attapulgite Scaffolds with Good Performance for Bone Regeneration.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Sep 22;15:6945-6960. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S254094. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33061361 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmaceutical electrospinning and 3D printing scaffold design for bone regeneration.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021 Jul;174:504-534. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2021.05.007. Epub 2021 May 13. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021. PMID: 33991588 Review.
-
Strategies of immobilizing BMP-2 with 3D-printed scaffolds to improve osteogenesis.Regen Med. 2023 May;18(5):425-441. doi: 10.2217/rme-2022-0222. Epub 2023 Apr 26. Regen Med. 2023. PMID: 37125508 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of BMP in Bone Tissue Engineering.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Mar 31;10:810880. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.810880. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35433652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Applications of Cell-Scaffold Constructs for Bone Regeneration Therapy.Cells. 2021 Oct 8;10(10):2687. doi: 10.3390/cells10102687. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of a Granular Bone Substitute for Bone Regeneration Using an Optimized In Vivo Alveolar Cleft Model.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Sep 2;10(9):1035. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10091035. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760137 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-196a-5p overexpression in Wharton's jelly umbilical cord stem cells promotes their osteogenic differentiation and new bone formation in bone defects in the rat calvarium.Cell Tissue Res. 2022 Nov;390(2):245-260. doi: 10.1007/s00441-022-03673-2. Epub 2022 Aug 4. Cell Tissue Res. 2022. PMID: 35925405
-
Stem Cell-Based Tissue Engineering for Cleft Defects: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2024 Sep;61(9):1439-1460. doi: 10.1177/10556656231175278. Epub 2023 May 18. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2024. PMID: 37203174 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meyer, U. & Wiesmann, H. P. Bone and Cartilage Engineering. (2006).
-
- Hench, L. L., Wilson, J. & Merwin, G. Bioglass™ Implants for Otology. (1984).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

