Prevalence of DSM-IV Alcohol Abuse and Dependence: United States, 1992
- PMID: 31798130
- PMCID: PMC6876405
Prevalence of DSM-IV Alcohol Abuse and Dependence: United States, 1992
Abstract
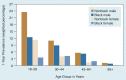
For the first time, results are presented on the prevalence of alcohol abuse and dependence in the United States in 1992, according to the most recent psychiatric classification of alcohol-related disorders from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition (DSM-IV). More than 7 percent of adults surveyed met DSM-IV criteria for 1-year alcohol abuse, alcohol dependence, or both. Males were almost three times more likely than females to meet the criteria for alcohol abuse and/or dependence; however, the male-to-female ratio was lowest in the youngest age group among nonblack respondents, suggesting that the rates of these disorders in nonblack females may be catching up.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Third Edition. Washington, DC: the Association; 1980.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Third Edition, Revised. Washington, DC: the Association; 1987.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. DSM–IV Options Book. Washington, DC: the Association; 1991.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Fourth Edition. Washington, DC: the Association; 1994.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous