NMDAR and JNK Activation in the Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus Caudalis Contributes to Masseter Hyperalgesia Induced by Stress
- PMID: 31798413
- PMCID: PMC6868050
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00495
NMDAR and JNK Activation in the Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus Caudalis Contributes to Masseter Hyperalgesia Induced by Stress
Abstract
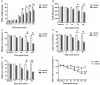
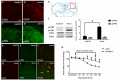
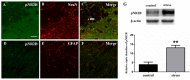
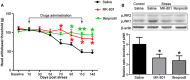
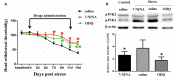
It is commonly accepted that psychological stress is closely associated with the occurrence and development of chronic orofacial pain. However, the pathogenesis underlying this process has not been fully elucidated. In the present study, we explored the role of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) and Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) mediated intercellular communication between neurons and astrocytes in the spinal trigeminal nucleus caudalis (Vc) in the induction of masseter hyperalgesia by psychological stress in rats. We found that subjecting rats to 14 days of restraint stress (8 h/d) caused a significant decrease in body weight gain, behavioral changes and marked masseter hyperalgesia in the rats. We also found that exposure to restraint stress for 14 days caused the expression of pJNK in astrocytes in the Vc to significantly increase, and intrathecally infusing a JNK inhibitor significantly prevented restraint stress-induced masseter hyperalgesia in the rats. In addition, after exposure to restraint stress for 14 days, the stressed group exhibited a noticeably increased expression level of pNR2B in neurons in the Vc. Then, we intrathecally injected MK-801 (an NMDAR inhibitor) and ifenprodil (a selective NR2B subunit antagonist) and observed that the two types of inhibitors not only alleviated masseter hyperalgesia but also significantly inhibited the phosphorylation of JNK in the Vc after restraint stress; this indicates that the effect of NMDAR antagonists may influence the activation of astrocytic JNK. Furthermore, inhibitors of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) activation and guanylate cyclase (GC) inhibitor could not only inhibit the expression of pJNK in the Vc, but also effectively alleviate masseter hyperalgesia induced by restraint stress. Taken together, our results suggest that NMDAR activation could increase JNK phosphorylation in astrocytes after restraint stress, which may depend on the nNOS-GC pathway. The intercellular communication between neurons and astrocytes in the Vc may play a key role in the induction of masseter muscle hyperalgesia by psychological stress in rats.
Keywords: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; c-Jun N- terminal kinase; chronic masseter pain; intercellular communication; psychological stress; spinal trigeminal nucleus caudalis.
Copyright © 2019 Lin, Zhao, Cheng, Zhao, Miao, Li, Chen and Zhang.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

