Feasibility of an at-home, web-based, interactive exercise program for older adults
- PMID: 31799367
- PMCID: PMC6883315
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trci.2019.10.005
Feasibility of an at-home, web-based, interactive exercise program for older adults
Abstract
Introduction: Increased physical exercise is linked to enhanced brain health and reduced dementia risk. Exercise intervention studies usually are conducted at facilities in groups under trainer supervision. To improve scalability, accessibility, and engagement, programs may need to be structured such that individuals can execute and adjust routines in their own homes.
Methods: One hundred eighty-three healthy older adults from two sites (the United States and Sweden) were screened. One hundred fifty-six subjects (mean age 73.2), randomly assigned to one of four interventions (PACE-Yourself physical exercise program, mindfulness meditation, or Cogmed® adaptive or nonadaptive computerized working memory training) began the study. All interventions were structurally similar: occurring in subjects' homes using interactive, web-based software, over five weeks, ∼175 minutes/week. In the PACE-Yourself program, video segments presented aerobic exercises at different pace and intensity (P&I). The program paused frequently, allowing subjects to indicate whether P&I was "too easy," "too hard," or "somewhat hard." P&I of the subsequent exercise set was adjusted, allowing subjects to exercise at a perceived exertion level of "somewhat hard." Program completion was defined as finishing ≥60% of sessions.
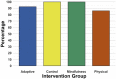
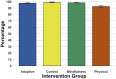
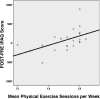
Results: A high percentage of participants in all groups completed the program, although the number (86%) was slightly lower in the PACE-Yourself group than the other three. Excluding dropouts, the PACE-Yourself group had a lower adherence rate of 93%, compared with the other three (∼98%). Over the five weeks, PACE-Yourself participants increased exercising at the highest intensity level, consistent with augmented aerobic activity over time. The number of exercise sessions completed predicted the postintervention versus preintervention increase in self-reported level of physical activity.
Discussion: This study supports the feasibility of a home-based, subject-controlled, exercise program in which P&I is regulated via real-time participant feedback, which may promote self-efficacy. Further study is needed to determine if similar results are found over longer periods and in more diverse populations.
Keywords: Adherence; At-home; Brain health; Dementia risk; Feasibility; Interactive; Older adults; Physical exercise program; Self-efficacy; Web-based.
Figures
References
-
- Larson E.B., Wang L., Bowen J.D., McCormick W.C., Teri L., Crane P. Exercise is associated with reduced risk for incident dementia among persons 65 years of age and older. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144:73–81. - PubMed
-
- Hartescu I., Morgan K., Stevinson C.D. Increased physical activity improves sleep and mood outcomes in inactive people with insomnia: a randomized controlled trial. J Sleep Res. 2015;24:526–534. - PubMed
-
- Sherrington C., Whitney J.C., Lord S.R., Herbert R.D., Cumming R.G., Close J.C. Effective exercise for the prevention of falls: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008;56:2234–2243. - PubMed
-
- Miele E.M., Headley S.A.E. The effects of chronic aerobic exercise on cardiovascular risk factors in persons with diabetes mellitus. Curr Diab Rep. 2017;17:97. - PubMed
-
- Mucke M., Ludyga S., Colledge F., Gerber M. Influence of regular physical activity and fitness on stress reactivity as measured with the trier social stress test protocol: a systematic review. Sports Med. 2018;48:2607–2622. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
