Trends in use, pharmacology, and clinical applications of emerging herbal nutraceuticals
- PMID: 31799702
- PMCID: PMC7056462
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.14943
Trends in use, pharmacology, and clinical applications of emerging herbal nutraceuticals
Abstract
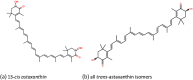
The nutraceuticals market is vast, encompassing many different products with inconsistent levels of evidence available to support their use. This overview represents a Western perspective of the nutraceuticals market, with a brief comparison with that in China, as an illustration of how individual health supplements increase and decrease in popularity in regional terms. Recent changes in sales patterns, mainly taken from the US market, are summarized and a selection of five newer products, which have not been subject to extensive recent review are profiled: astaxanthin, a carotenoid found in red algae, seafood, salmon and trout, as an antioxidant; cannabidiol, a non-euphoric marijuana ingredient used as mood enhancer and for painful/inflammatory conditions; modified extracts of ginseng used in new indications including dementia and space travel; monk fruit, a non-sugar high intensity sweetener and nigella seed, a popular food ingredient and Asian medicine, which has experienced an extraordinary rise in sales recently. LINKED ARTICLES: This article is part of a themed section on The Pharmacology of Nutraceuticals. To view the other articles in this section visit http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bph.v177.6/issuetoc.
© 2019 The British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical