The IL-2RG R328X nonsense mutation allows partial STAT-5 phosphorylation and defines a critical region involved in the leaky-SCID phenotype
- PMID: 31799703
- PMCID: PMC7066387
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.13405
The IL-2RG R328X nonsense mutation allows partial STAT-5 phosphorylation and defines a critical region involved in the leaky-SCID phenotype
Abstract
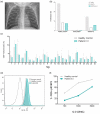
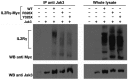
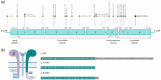
In addition to their detection in typical X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency, hypomorphic mutations in the interleukin (IL)-2 receptor common gamma chain gene (IL2RG) have been described in patients with atypical clinical and immunological phenotypes. In this leaky clinical phenotype the diagnosis is often delayed, limiting prompt therapy in these patients. Here, we report the biochemical and functional characterization of a nonsense mutation in exon 8 (p.R328X) of IL2RG in two siblings: a 4-year-old boy with lethal Epstein-Barr virus-related lymphoma and his asymptomatic 8-month-old brother with a Tlow B+ natural killer (NK)+ immunophenotype, dysgammaglobulinemia, abnormal lymphocyte proliferation and reduced levels of T cell receptor excision circles. After confirming normal IL-2RG expression (CD132) on T lymphocytes, signal transducer and activator of transcription-1 (STAT-5) phosphorylation was examined to evaluate the functionality of the common gamma chain (γc ), which showed partially preserved function. Co-immunoprecipitation experiments were performed to assess the interaction capacity of the R328X mutant with Janus kinase (JAK)3, concluding that R328X impairs JAK3 binding to γc . Here, we describe how the R328X mutation in IL-2RG may allow partial phosphorylation of STAT-5 through a JAK3-independent pathway. We identified a region of three amino acids in the γc intracellular domain that may be critical for receptor stabilization and allow this alternative signaling. Identification of the functional consequences of pathogenic IL2RG variants at the cellular level is important to enable clearer understanding of partial defects leading to leaky phenotypes.
Keywords: IL-2RG; JAK1; JAK3; STAT-5; X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency; hypomorphic mutations; interleukin receptor common gamma subunit; leaky SCID; whole exome sequencing.
© 2019 British Society for Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no commercial or financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Takeshita T, Asao H, Ohtani K et al Cloning of the gamma chain of the human IL‐2 receptor. Science 1992; 257:379–82. - PubMed
-
- Noguchi M, Yi H, Rosenblatt HM et al Interleukin‐2 receptor gamma chain mutation results in X‐linked severe combined immunodeficiency in humans. Cell 1993; 73:147–57. - PubMed
-
- Puck JM, Deschênes SM, Porter JC et al The interleukin‐2 receptor gamma chain maps to Xq13.1 and is mutated in X‐linked severe combined immunodeficiency, SCIDX1. Hum Mol Genet 1993; 2:1099–104. - PubMed
-
- Habib T, Senadheera S, Weinberg K, Kaushansky K. The common γ chain (γc) is a required signaling component of the IL‐21 receptor and supports IL‐21‐induced cell proliferation via JAK3 †. Biochemistry 2002; 41:8725–31. - PubMed
-
- Walshe D, Gaspar HB, Thrasher AJ, Cale CM, Gilmour KC. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 tyrosine phosphorylation for the diagnosis and monitoring of patients with severe combined immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2009; 123:505–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

