Baseline patient-reported outcomes from UNITE: an observational, international, multicentre registry to evaluate hidradenitis suppurativa in clinical practice
- PMID: 31800124
- PMCID: PMC7317945
- DOI: 10.1111/jdv.16132
Baseline patient-reported outcomes from UNITE: an observational, international, multicentre registry to evaluate hidradenitis suppurativa in clinical practice
Abstract
Background: Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic, inflammatory, skin condition associated with many comorbidities and often has a substantial impact on patients' lives.
Objectives: To evaluate symptom burden and health-related quality of life (HRQoL) at baseline in patients with HS in an observational, real-world, clinical setting using several tools including a validated HS-specific instrument.
Methods: This study evaluated HRQoL data from the international UNITE HS disease registry. Administration of patient-reported outcome (PRO) instruments and collection of data were executed per local regulations. All data were assessed using descriptive statistical methods.
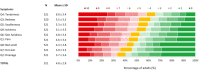
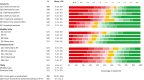
Results: PRO data from 529 adults and 65 adolescents were evaluated. Most adults (64.5%) and adolescents (73.8%) were classified as Hurley Stage II with substantial disease burden at baseline. HS had a large effect (mean DLQI = 12.6) and moderate effect (mean CDLQI = 6.9) on the lives of adults and adolescents, respectively. Approximately 58% of adults and 41% of adolescents had anxiety scores beyond the normal range; 30% of adults and 16% of adolescents exhibited symptoms of depression. Based on HSSA and HSIA scores, approximately 30% of adults reported a substantial burden of multiple HS clinical symptoms and more than 45% reported a significant emotional impact of HS that adversely affected their intimate relationships. Only 60% of adults were employed and of those, 64% reported at least some degree of impairment while working because of HS.
Conclusions: Based on PROs collected from patients enrolled in the UNITE registry, a real-world, clinical setting, HS has a significant negative impact on the everyday lives of patients affected by this disease.
© 2019 AbbVie Inc. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Figures
References
-
- van der Zee HH, Jemec GB. New insights into the diagnosis of hidradenitis suppurativa: clinical presentations and phenotypes. J Am Acad Dermatol 2015; 73: S23–S26. - PubMed
-
- Jemec GB. Clinical practice. Hidradenitis suppurativa. N Engl J Med 2012; 366: 158–164. - PubMed
-
- Alikhan A, Lynch PJ, Eisen DB. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a comprehensive review. J Am Acad Dermatol 2009; 60: 539–561; quiz 62–3. - PubMed
-
- Buimer MG, Wobbes T, Klinkenbijl JH. Hidradenitis suppurativa. Br J Surg 2009; 96: 350–360. - PubMed
-
- Shah N. Hidradenitis suppurativa: a treatment challenge. Am Fam Physician 2005; 72: 1547–1552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

