Gene expression is associated with virulence in murine macrophages infected with Leptospira spp
- PMID: 31800570
- PMCID: PMC6892507
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225272
Gene expression is associated with virulence in murine macrophages infected with Leptospira spp
Abstract
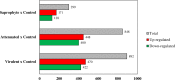
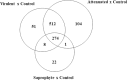
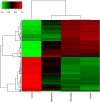
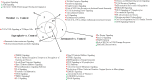
Leptospira genus contains species that affect human health with varying degrees of pathogenicity. In this context, we aimed to evaluate the differences in the modulation of host gene expression by strains of Leptospira varying in virulence. Our data showed a high number of differentially expressed transcripts in murine macrophages following 6h of infection. Leptospira infection modulated a set of genes independently of their degree of virulence. However, pathway analysis indicated that Apoptosis, ATM Signaling, and Cell Cycle: G2/M DNA Damage Checkpoint Regulation were exclusively regulated following infection with the virulent strain. Taken together, results demonstrated that species and virulence play a role during host response to Leptospira spp in murine macrophages, which could contribute to understanding the pathogenesis of leptospirosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

