c-Jun overexpression in CAR T cells induces exhaustion resistance
- PMID: 31802004
- PMCID: PMC6944329
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1805-z
c-Jun overexpression in CAR T cells induces exhaustion resistance
Abstract
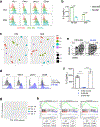
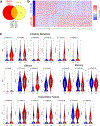
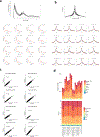
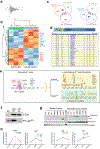
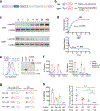
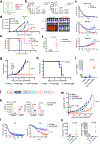
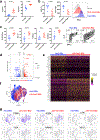
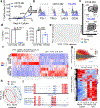
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells mediate anti-tumour effects in a small subset of patients with cancer1-3, but dysfunction due to T cell exhaustion is an important barrier to progress4-6. To investigate the biology of exhaustion in human T cells expressing CAR receptors, we used a model system with a tonically signaling CAR, which induces hallmark features of exhaustion6. Exhaustion was associated with a profound defect in the production of IL-2, along with increased chromatin accessibility of AP-1 transcription factor motifs and overexpression of the bZIP and IRF transcription factors that have been implicated in mediating dysfunction in exhausted T cells7-10. Here we show that CAR T cells engineered to overexpress the canonical AP-1 factor c-Jun have enhanced expansion potential, increased functional capacity, diminished terminal differentiation and improved anti-tumour potency in five different mouse tumour models in vivo. We conclude that a functional deficiency in c-Jun mediates dysfunction in exhausted human T cells, and that engineering CAR T cells to overexpress c-Jun renders them resistant to exhaustion, thereby addressing a major barrier to progress for this emerging class of therapeutic agents.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS
C.L.M., R.C.L., E.W.W. and E.S. are inventors on a Stanford University Provisional patent pending on modulating AP-1 to enhance function of T cells; 62/599,299; C.L.M. is a founder of, holds equity in and receives consulting fees from Lyell Immunopharma, which has licensed the technology. R.C.L. is employed by and E.W.W. and E.S. are consultants for Lyell Immunopharma.
Figures








Comment in
-
Overcoming CAR T cell exhaustion.Nat Rev Immunol. 2020 Feb;20(2):72-73. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0265-x. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020. PMID: 31844329 No abstract available.
-
Prevention of CAR-T-cell dysfunction.Nat Biomed Eng. 2020 Jan;4(1):16-17. doi: 10.1038/s41551-019-0512-2. Nat Biomed Eng. 2020. PMID: 31911621 No abstract available.
-
Next-Generation CAR T Cells Counter Exhaustion.Cancer Discov. 2020 Feb;10(2):166-167. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-NB2019-146. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Cancer Discov. 2020. PMID: 31915194
References
REFERENCES FOR METHODS
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

