Reduced microRNA 375 in colorectal cancer upregulates metadherin-mediated signaling
- PMID: 31802830
- PMCID: PMC6886017
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i44.6495
Reduced microRNA 375 in colorectal cancer upregulates metadherin-mediated signaling
Abstract
Background: The human microRNA 375 (MIR375) is significantly downregulated in human colorectal cancer (CRC) and we have previously shown that MIR375 is a CRC-associated miRNA. The metadherin (MTDH) is a candidate target gene of MIR375.
Aim: To investigate the interaction and function between MIR375 and MTDH in human CRC.
Methods: A luciferase reporter system was used to confirm the effect of MIR375 on MTDH expression. The expression levels of MIR375 and the target genes were evaluated by quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR), western blotting, or immunohistochemistry.
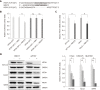
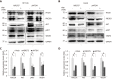
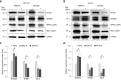
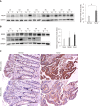
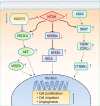
Results: MTDH expression was found to be upregulated in human CRC tissues compared to that in healthy controls. We show that MIR375 regulates the expression of many genes involved in the MTDH-mediated signal transduction pathways [BRAF-MAPK and phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate-3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA)-AKT] in CRC cells. Upregulated MTDH expression levels were found to inhibit NF-κB inhibitor alpha, which further upregulated NFKB1 and RELA expression in CRC cells.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that suppressing MIR375 expression in CRC regulates cell proliferation and angiogenesis by increasing MTDH expression. Thus, MIR375 may be of therapeutic value in treating human CRC.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Cell proliferation; Colorectal cancer; Metadherin; MicroRNA 375; Mitogen-activated protein kinase.
©The Author(s) 2019. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Greenlee RT, Hill-Harmon MB, Murray T, Thun M. Cancer statistics, 2001. CA Cancer J Clin. 2001;51:15–36. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Fearon ER. Molecular genetics of colorectal cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 2011;6:479–507. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

