Burn-Induced Coagulopathies: a Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 31804296
- PMCID: PMC7439938
- DOI: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001484
Burn-Induced Coagulopathies: a Comprehensive Review
Abstract
Burn-induced coagulopathy is not well understood, and consensus on diagnosis, prevention, and treatments are lacking. In this review, literature on burn-induced (and associated) coagulopathy is presented along with the current understanding of the effects of burn injury on the interactions among coagulation, fibrinolysis, and inflammation in the acute resuscitative phase and reconstructive phase of care. The role of conventional tests of coagulopathy and functional assays like thromboelastography or thromboelastometry will also be discussed. Finally, reported methods for the prevention and treatment of complications related to burn-induced coagulopathy will be reviewed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
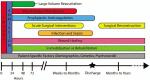
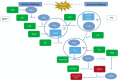
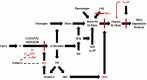
References
-
- Stensballe J, Henriksen HH, Johansson PI. Early haemorrhage control and management of trauma-induced coagulopathy: the importance of goal-directed therapy. Curr Opin Crit Care 23:503–510, 2017. - PubMed
-
- Shupp JW, Brummel-Ziedins KE, Cohen MJ, Freeman K, Hammamieh R, Mudunuri US, Orfeo T, Moffatt LT, Brownstein BH, Mann KG, et al. Military supplement: assessment of coagulation homeostasis in blunt, penetrating, and thermal trauma: guidance for a multi-center systems biology approach. Shock 52: 1S Suppl 1: 84–91, 2019. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zeeshan M, Hamidi M, Kulvatunyou N, Jehan F, O’Keeffe T, Khan M, Rashdan L, Tang A, Zakaria E-R, Joseph B. 3-factor versus 4-factor pcc in coagulopathy of trauma: four is better than three. Shock 52:23–28, 2019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

