A randomized controlled trial on analgesic effect of repeated Quadratus Lumborum block versus continuous epidural analgesia following laparoscopic nephrectomy
- PMID: 31805855
- PMCID: PMC6894195
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-019-0891-7
A randomized controlled trial on analgesic effect of repeated Quadratus Lumborum block versus continuous epidural analgesia following laparoscopic nephrectomy
Abstract
Background: Epidural analgesia as the effective pain management for abdominal surgery has side effects such as paresthesia, hypotension, hematomas, and impaired motoric of lower limbs. The quadratus lumborum block (QLB) has potential as an abdominal truncal block, however, its analgesic efficacy has never been compared to epidural analgesia on laparoscopic nephrectomy. This prospective randomized controlled study compared the effectiveness of QLB with the epidural analgesia technique in relieving postoperative pain following transperitoneal laparoscopic nephrectomy.
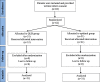
Methods: Sixty-two patients underwent laparoscopic donor nephrectomy and were randomized to receive QLB (n = 31) or continuous epidural (n = 31). The QLB group received bilateral QLB using 0.25% bupivacaine and the epidural group received 6 ml/h of 0.25% bupivacaine for intraoperative analgesia. As postoperative analgesia, the QLB group received repeated bilateral QLB with the same dose and the epidural group received 6 ml/h of 0.125% bupivacaine for 24 h after surgery completion. The primary outcome was the 24-h cumulative morphine requirement after surgery. The secondary outcome was the postoperative pain scores. Sensory block coverage, hemodynamic changes, Bromage score, postoperative nausea-vomiting (PONV), paresthesia, and duration of urinary catheter usage were recorded and analyzed.
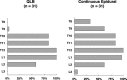
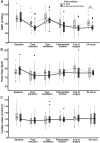
Result: The 24-h cumulative morphine requirement and pain scores after surgery were comparable between the QLB and epidural groups. The coverage of QLB was extended from T9 to L2 and the continuous epidural block was extended from T8 to L3 dermatomes. The mean arterial pressure (MAP) measured at 24 h after surgery was lower in the epidural group (p = 0.001). Bromage score, incidence of PONV, and paresthesia were not significantly different between the two groups. Duration of urinary catheter usage was shorter (p < 0.001) in the QLB group.
Conclusion: The repeated QLB had a similar 24-h cumulative morphine requirement, comparable postoperative pain scores and sensory blockade, higher postoperative MAP, a similar degree of motoric block, no difference in the incidence of PONV and paresthesia, and shorter urinary catheter usage, compared to the continuous epidural analgesia following transperitoneal laparoscopic nephrectomy.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrial.gov NCT03520205 retrospectively registered on May 9th 2018.
Keywords: Epidural analgesia; Laparoscopic nephrectomy; Patient-controlled analgesia; Postoperative analgesia; Quadratus lumborum block.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Analgesic effect of the ultrasound-guided subcostal approach to transmuscular quadratus lumborum block in patients undergoing laparoscopic nephrectomy: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Anesthesiol. 2019 Aug 14;19(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12871-019-0825-4. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019. PMID: 31412770 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Transmuscular quadratus lumborum (TQL) block for laparoscopic colorectal surgery: study protocol for a double-blind, prospective randomized placebo-controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Jun 26;21(1):581. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04525-6. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32586361 Free PMC article.
-
Quadratus lumborum block vs. transversus abdominis plane block for postoperative pain control in patients with nephrectomy: A systematic review and network meta-analysis.J Clin Anesth. 2024 Aug;95:111453. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2024.111453. Epub 2024 Mar 25. J Clin Anesth. 2024. PMID: 38531283
-
Quadratus Lumborum Block with Laparoscopic Assisted Catheter Placement Technique in Donor Nephrectomy: A Preliminary Report.Transplant Proc. 2022 Sep;54(7):1759-1762. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2022.05.018. Epub 2022 Jul 19. Transplant Proc. 2022. PMID: 35863995
-
Comparing the analgesic effect of regional nerve block technique in laparoscopic nephrectomy: A systematic review and network meta-analysis.J Clin Anesth. 2025 Apr;103:111829. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2025.111829. Epub 2025 Apr 7. J Clin Anesth. 2025. PMID: 40199032
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Analgesia Effect after Ultrasound-Guided Laparoscopic Renal Surgery.Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Dec 24;2021:6194806. doi: 10.1155/2021/6194806. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Dec 8;2022:9864768. doi: 10.1155/2022/9864768. PMID: 34976111 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized controlled trial of a quadratus lumborum block with liposomal bupivacaine for postoperative analgesia in laparoscopic donor nephrectomy.Clin Transplant. 2021 Sep;35(9):e14403. doi: 10.1111/ctr.14403. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Clin Transplant. 2021. PMID: 34184312 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The efficacy and safety of continuous transmuscular quadratus lumborum block for postoperative analgesia after laparoscopic nephrectomy: A prospective randomized clinical trial.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2025 Jan-Mar;41(1):158-163. doi: 10.4103/joacp.joacp_469_23. Epub 2025 Jan 23. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40026741 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Ultrasound-Guided Retrolaminar Block and Erector Spinae Plane Block in Retroperitoneal Laparoscopic Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Pain Res. 2022 Mar 28;15:815-826. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S349028. eCollection 2022. J Pain Res. 2022. PMID: 35370419 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-guided peripheral trunk block technique: A new approach gradually stepping onto the stage of clinical anesthesia.Ibrain. 2021 Sep 28;7(3):211-226. doi: 10.1002/j.2769-2795.2021.tb00085.x. eCollection 2021 Sep. Ibrain. 2021. PMID: 37786802 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wibisono Elita, Mochtar Chaidir Arif, Hamid Agus Rizal A. H, Widia Fina, Sukmono R. Besthadi, Wahyudi Irfan. Laparoscopic Living Donor Nephrectomy in Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital: Postoperative Pain and Recovery Analysis. Advanced Science Letters. 2018;24(9):6704–6708. doi: 10.1166/asl.2018.12816. - DOI
-
- Sahajananda H. Jyothi, Punithavathy. Renal transplantation with and without epidural analgesia. Indian J Anesth. 2006;50(3):187–192.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

