RNA m6A Methyltransferase METTL3 Promotes The Growth Of Prostate Cancer By Regulating Hedgehog Pathway
- PMID: 31806999
- PMCID: PMC6842310
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S226796
RNA m6A Methyltransferase METTL3 Promotes The Growth Of Prostate Cancer By Regulating Hedgehog Pathway
Abstract
Purpose: N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant internal modification on eukaryotic mRNA and gained increasing attention recently. More and more evidence suggest that m6A methylation plays crucial role in tumor genesis and development. However, its role in prostate cancer remains largely unknown.
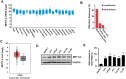
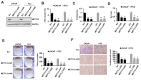
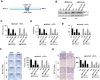
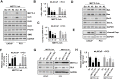
Methods: METTL3 expression status in prostate cancer was analyzed by using TCGA database and Western blotting. m6A content was analyzed by using RNA Methylation Quantification Kit. The role of METTL3 in prostate cancer cells was determined by proliferation, survival, colony formation, and invasion assays. The m6A level of GLI1 RNA was detected by methylated RNA immunoprecipitation (MeRIP) assay. In vivo role of METTL3 was studied on xenograft models.
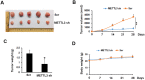
Results: We found that m6A methyltransferase METTL3 was overexpressed in prostate cancer cell lines, together with increased m6A content. Functionally, silencing of METTL3 by shRNA in prostate cancer cell lines resulted in decreased m6A content, cell proliferation, survival, colony formation, and invasion. Interestingly, overexpression of wild-type METTL3 abrogated the repression effect of METTL3 depletion on m6A content, cell proliferation, survival, colony formation, and invasion, while the overexpression of m6A catalytic site mutant METTL3 was unable to rescue the inhibitory effect caused by METTL3 depletion. Further mechanism analysis demonstrated that METTL3 silence decreased the m6A modification and expression of GLI1, an important component of hedgehog pathway, which led to cell apoptosis. Moreover, depletion of METTL3 inhibited tumor growth in vivo.
Conclusion: Our results suggested that the m6A methyltransferase METTL3 promotes the growth and motility of prostate cancer cells by regulating hedgehog pathway.
Keywords: GLI1; METTL3; RNA methylation; hedgehog; prostate cancer.
© 2019 Cai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest in this work.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

