circ_0003418 Inhibits Tumorigenesis And Cisplatin Chemoresistance Through Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway In Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 31807029
- PMCID: PMC6857737
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S229507
circ_0003418 Inhibits Tumorigenesis And Cisplatin Chemoresistance Through Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway In Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Accumulating evidences indicate that circRNAs play important roles in the progression and chemoresistance of human cancers. The present study is designated for researching the roles of circ_0003418 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods: We detected the expression profile of circ_0003418 in human HCC tissues and cell lines by quantitative real-time-PCR assays. CCK-8 assay, transwell migration assay, transwell invasion assay and drug-sensitivity analysis were carried out to estimate the effects of circ_0003418 on HCC cells' proliferation, migration, invasion and resistance to cisplatin, respectively. Mouse xenograft model was conducted to monitor the role of circ_0003418 in cisplatin resistance in vivo. Western blotting was performed to explore the changes of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway after knockdown of circ_0003418. The rescue experiment was carried out to explore circ_0003418-activated biological functions through Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
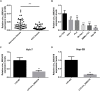
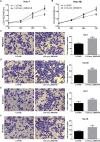
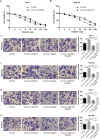
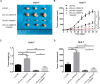
Results: The expression level of circ_0003418 was downregulated in HCC tissues and cell lines, and the level correlated with tumor size, TNM stage and HBsAg level in HCC patients. circ_0003418 knockdown promoted HCC cells' proliferation, migration, and invasion. Additionally, suppression of circ_0003418 enhanced cisplatin resistance of HCC cells in vivo and vitro. Knockdown of circ_0003418 activated the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway in HCC cells. The effect of circ-0003418 on sensitivity of HCC cells to cisplatin was reversed after inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
Conclusion: circ-0003418 exerts an antitumorigenic role in HCC and advances the sensitivity of HCC cells to cisplatin by restraining the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Thus, circ-0003418 may represent a novel biomarker and provide us a new strategy for the treatment of HCC.
Keywords: Wnt/β-catenin; circ-0003418; circRNA; cisplatin resistance; hepatocellular carcinoma.
© 2019 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Circular RNA Hsa_circ_0004018 Inhibits Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway by Targeting microRNA-626/DKK3 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Sep 22;13:9351-9364. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S254997. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 33061423 Free PMC article.
-
CircRNA circ_0067934 promotes tumor growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma through regulation of miR-1324/FZD5/Wnt/β-catenin axis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Mar 4;497(2):626-632. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.119. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29458020
-
Enhanced expression of circular RNA hsa_circ_000984 promotes cells proliferation and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer by modulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Apr;23(8):3366-3374. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201904_17700. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31081091
-
A spotlight on the interplay between Wnt/β-catenin signaling and circular RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma progression.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 21;13:1224138. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1224138. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37546393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling as a Driver of Stemness and Metabolic Reprogramming in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 7;14(21):5468. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215468. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358885 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circ-PRKDC Contributes to 5-Fluorouracil Resistance of Colorectal Cancer Cells by Regulating miR-375/FOXM1 Axis and Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Jun 23;13:5939-5953. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S253468. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32606803 Free PMC article.
-
CircFMN2 Boosts Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via Upregulating CNBP by Restraining Ubiquitination.J Oncol. 2022 Jul 21;2022:2674163. doi: 10.1155/2022/2674163. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35909906 Free PMC article.
-
The Underlying Mechanisms of Noncoding RNAs in the Chemoresistance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Sep 4;21:13-27. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.05.011. Epub 2020 May 15. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 32505000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent progress in treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Sep 1;10(9):2993-3036. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33042631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs: new biomarkers of chemoresistance in cancer.Cancer Biol Med. 2021 Mar 19;18(2):421-36. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0312. Cancer Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33738995 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:1–31. - PubMed
-
- Rudolph C, Melau C, Nielsen JE, et al. Involvement of the DNA mismatch repair system in cisplatin sensitivity of testicular germ cell tumours. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2017;40(4):341‐355. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

