Carcinoembryonic antigen related cell adhesion molecule 6 promotes the proliferation and migration of renal cancer cells through the ERK/AKT signaling pathway
- PMID: 31807423
- PMCID: PMC6842788
- DOI: 10.21037/tau.2019.09.02
Carcinoembryonic antigen related cell adhesion molecule 6 promotes the proliferation and migration of renal cancer cells through the ERK/AKT signaling pathway
Abstract
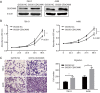
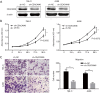
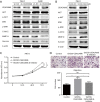
Background: Carcinoembryonic antigen related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) is a versatile glycoprotein and a member of the CEACAM family. Studies suggested that it served as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in some malignancies. In addition, it is involved in tumorigenesis by stimulating proliferation, suppressing apoptosis, facilitating migration and invasion, promoting angiogenesis, and inducing drug resistance. In the present study, we demonstrated the oncogenic effects of CEACAM6 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC).
Methods: CEACAM6 expression was detected by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), immunohistochemical staining and western blot in ccRCC tumor tissues and cell lines. Survival analysis was performed using the data of TCGA database. Cell proliferation and migration were detected by CCK-8 and transwell assays with the overexpression or silencing of CEACAM6. LY294002 was used to block the activation of PI3K/AKT pathway. Associated pathway proteins were detected by western blot.
Results: CEACAM6 was upregulated in ccRCC cell lines and tumor tissues. Longer overall survival was observed in patients with relatively low CEACAM6 levels. Furthermore, overexpression of CEACAM6 promoted the proliferation and migration of ccRCC cells. Conversely, shRNA-mediated CEACAM6 depletion modulated those changes. Further investigation demonstrated that the ERK/AKT signaling pathway activation played a pivotal role. In addition, PI3K/AKT pathway blockade abrogated the effects of CEACAM6 overexpression.
Conclusions: Aberrantly high expression of CEACAM6 is a stimulus for the formation and progression of ccRCC.
Keywords: Carcinoembryonic antigen related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6); clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC); migration; proliferation.
2019 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The emerging roles of CEACAM6 in human cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Mar;64(3):27. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5615. Epub 2024 Jan 19. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38240103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CEACAM6 promotes cholangiocarcinoma migration and invasion by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition through inhibition of the SRC/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Oncol Lett. 2022 Jan;23(1):39. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.13157. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 34966455 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-Coding RNA LUCAT1 Promotes Proliferation and Invasion in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Through AKT/GSK-3β Signaling Pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(3):891-904. doi: 10.1159/000491957. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30032137
-
Effect of CEACAM6 silencing on the biological behavior of human gallbladder cancer cells.Oncol Lett. 2020 Sep;20(3):2677-2688. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11806. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32782584 Free PMC article.
-
Towards understanding the mechanisms of actions of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 in cancer progression.Cancer Sci. 2018 Jan;109(1):33-42. doi: 10.1111/cas.13437. Epub 2018 Jan 2. Cancer Sci. 2018. PMID: 29110374 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The emerging roles of CEACAM6 in human cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2024 Mar;64(3):27. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2024.5615. Epub 2024 Jan 19. Int J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38240103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The m6A modification-mediated OGDHL exerts a tumor suppressor role in ccRCC by downregulating FASN to inhibit lipid synthesis and ERK signaling.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Aug 25;14(8):560. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06090-7. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37626050 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Exposure of Renal Progenitor Cells (HRTPT) to As (III) Implicates Microfibril Associated Protein 5 (MFAP5) in the Activation of Carcinoembryonic Antigen Related Cell Adhesion Molecules (CEACAM 5 and 6).Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jun 12;47(6):455. doi: 10.3390/cimb47060455. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699854 Free PMC article.
-
HOXB5-activated ANGPT2 promotes the proliferation, migration, invasion and angiogenic effect of esophageal cancer cells via activating ERK/AKT signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Jul 20;24(3):585. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11522. eCollection 2022 Sep. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35949323 Free PMC article.
-
The role of long non-coding RNA FGD5-AS1 in cancer.Bioengineered. 2022 Apr;13(4):11026-11041. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2067292. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35475392 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Buti S, Bersanelli M, Sikokis A, et al. Chemotherapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma today? A systematic review. Anticancer Drugs 2013;24:535-54. - PubMed
-
- Osorio JC, Motzer RJ, Voss MH. Optimizing Treatment Approaches in Advanced Renal Cancer. Oncology (Williston Park) 2017;31:919-26, 928-30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
