Synergic effects of histology subtype, tumor size, and lymph node metastasis on distant metastasis in differentiated thyroid cancer
- PMID: 31807515
- PMCID: PMC6861801
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2019.09.137
Synergic effects of histology subtype, tumor size, and lymph node metastasis on distant metastasis in differentiated thyroid cancer
Abstract
Background: Detection of distant metastasis (DM) is important in differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC). This study aimed to investigate the synergic effects of histology subtype, tumor size, and lymph node metastasis (LNM) status on the occurrence of DM in DTC.
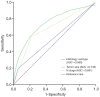
Methods: We collected data of 96,788 patients with DTC. Univariate and multivariate analyses were conducted to identify the risk factors of DM. Relative excess risk of synergic effect, attributable proportion of synergic effect, and synergy index were then calculated to assess synergic effects. Further, Kaplan-Meier method using the log-rank test and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were utilized.
Results: Age at diagnosis (P<0.001), sex (P<0.001), race (P<0.01), tumor size (P<0.001), N stage (P < 0.001), histology subtype (P<0.001), and extrathyroidal extension (P<0.001) were risk factors for DM in both univariate and multivariate analyses. We also found a significant additive synergic effect between histology subtype and LNM, and between tumor size and LNM on DM in the DTC patients. In addition, patients with follicular thyroid cancer and N1 stage had the sharpest decline in cancer-specific survival curves (P<0.001) and all-cause survival curves (P<0.001) compared to patients with other combinations of histology subtype and N stage. Similar results were obtained in patients with larger tumors (≥10 mm) and N1 stage. The areas under the curve of histology subtype, tumor size, and LNM status were 0.569, 0.744, and 0.681, respectively.
Conclusions: Age at diagnosis, sex, race, tumor size, N stage, histology subtype, and extrathyroidal extension are risk factors for DM in DTC patients. LNM has a synergic effect with either follicular thyroid histology or larger tumor size for higher risk of DM which is important for diagnosing DM.
Keywords: Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER); differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC); distant metastasis (DM); synergic effect.
2019 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
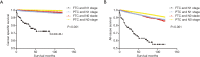
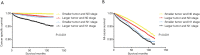
Similar articles
-
Synergic effects of histology subtype, lymph node metastasis, and distant metastasis on prognosis in differentiated thyroid carcinoma using the SEER database.Gland Surg. 2020 Aug;9(4):907-918. doi: 10.21037/gs-20-273. Gland Surg. 2020. PMID: 32953600 Free PMC article.
-
Innovative analysis of distant metastasis in differentiated thyroid cancer.Oncol Lett. 2020 Mar;19(3):1985-1992. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11304. Epub 2020 Jan 15. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32194693 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor size interpretation for predicting cervical lymph node metastasis using a differentiated thyroid cancer risk model.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Aug 12;9:5015-22. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S107187. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27574443 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Gross Strap Muscle Invasion on Outcome of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2020 Sep 25;10:1687. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01687. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33102203 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical, Pathological, and Molecular Characteristics Correlating to the Occurrence of Radioiodine Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2020 Sep 30;10:549882. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.549882. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33117686 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Can Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis Increase the Risk of Distant Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma?Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 24;13:917794. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.917794. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35813656 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term impact of delayed surgical treatment on the prognosis of patients with T1bN1-stage PTC: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Cancer. 2025 May 27;25(1):950. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14371-x. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40426087 Free PMC article.
-
Novel nomogram to predict risk of bone metastasis in newly diagnosed thyroid carcinoma: a population-based study.BMC Cancer. 2020 Nov 3;20(1):1055. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07554-1. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33143688 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive factors of lateral lymph node metastasis in conventional papillary thyroid carcinoma.Gland Surg. 2020 Aug;9(4):1000-1007. doi: 10.21037/gs-20-482. Gland Surg. 2020. PMID: 32953608 Free PMC article.
-
Nomogram individually predicts the risk for distant metastasis and prognosis value in female differentiated thyroid cancer patients: A SEER-based study.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 10;12:800639. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.800639. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36033442 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
