Wenshen decoction suppresses inflammation in IL-33-induced asthma murine model via inhibiting ILC2 activation
- PMID: 31807551
- PMCID: PMC6861797
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2019.09.34
Wenshen decoction suppresses inflammation in IL-33-induced asthma murine model via inhibiting ILC2 activation
Abstract
Background: Wenshen decoction, consisting of Epimedium brevicornu Maxim, Morinda officinalis How and Cnidium monnieri (L.) Cusson, has favorable efficacy in the treatment of asthma in China.
Methods: The present study investigated the potential immunomodulatory mechanism underlying the therapeutic effects of Wenshen decoction on mouse asthma.
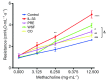
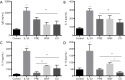
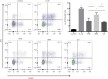
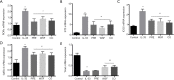
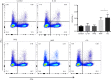
Results: Oral Wenshen decoction could ameliorate the production of IL-4, IL-5, IL-13 in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), reduce serum IgE, and improve the airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) and airway inflammation in the BALB/c mice after intranasal treatment with recombinant IL-33. Moreover, Wenshen decoction reduced ILC2 and RORα mRNA expression, decreased the mRNA expression of ICOS and ST2 in the lung, but significantly increased the production of IFN-γ.
Conclusions: Our study indicates that Wenshen decoction may inhibit the activation of ILC2 through the IL-33/ST2/ICOS pathway to further suppress airway inflammation and AHR in the asthmatic mice, and the increased IFN-γ might be related to the effects of Wenshen decoction on ILC2.
Keywords: Asthma; ILC2; Wenshen decoction; traditional Chinese medicine.
2019 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
