Effects of dietary butyrate supplementation and crude protein level on carcass traits and meat composition of broiler chickens
- PMID: 31807664
- PMCID: PMC6852878
- DOI: 10.5194/aab-62-527-2019
Effects of dietary butyrate supplementation and crude protein level on carcass traits and meat composition of broiler chickens
Abstract
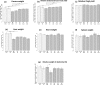
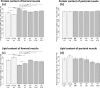
The short-chain fatty acid butyrate, either in unprotected or protected form, is widely applied as a growth-promoting feed additive in poultry nutrition; however, its possible effects on the carcass composition of broilers have not been fully elucidated. Further, lowering dietary crude protein (CP) levels is an important issue in poultry farming, contributing to ecologically beneficial lower nitrogen excretion. The main aims of this study were to test how unprotected and protected forms of butyrate and decreased dietary CP content with essential amino acid (lysine, methionine, threonine, tryptophan) supplementation ("LP-EAA" diet) affect carcass parameters and the chemical composition of muscles in broilers. Ross 308 chickens were randomized to seven groups ( /group) receiving adequate CP-containing (normal protein, "NP") or LP-EAA diets, both supplemented with or without unprotected sodium butyrate, and NP diets with different forms of protected sodium butyrate. Carcass traits were measured, and the chemical composition of pectoral and femoral muscles was analyzed at the age of 6 weeks. Carcass weight was significantly increased by the LP-EAA diet and all protected butyrate types tested, while the relative breast meat yield was significantly higher in LP-EAA than NP groups and in both unprotected and protected butyrate-supplemented chickens compared to controls. The protein content of the femoral muscle was significantly decreased, but its lipid content was significantly elevated by the LP-EAA diet and by all types of butyrate addition. However, no changes were detected in the chemical composition of pectoral muscle. In conclusion, breast meat production can be effectively stimulated by dietary factors, such as by reducing dietary CP content with essential amino acid supplementation and by applying butyrate as a feed additive, while its chemical composition remains unchanged, in contrast to the femoral muscle. The aforementioned nutritional strategies seem to be the proper tools to increase carcass yield and to alter meat composition of broilers, contributing to more efficient poultry meat production.
Copyright: © 2019 Gábor Mátis et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changes in body composition and meat quality in response to dietary amino acid provision in finishing broilers.Animal. 2019 May;13(5):1094-1102. doi: 10.1017/S1751731118002306. Epub 2018 Oct 5. Animal. 2019. PMID: 30289100
-
Effects of high peanut meal with different crude protein level supplemented with amino acids on performance, carcass traits and nitrogen retention of Chinese Yellow broilers.J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2016 Aug;100(4):657-64. doi: 10.1111/jpn.12420. Epub 2015 Dec 14. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2016. PMID: 27401885
-
The effects of conjugated linoleic acid on growth performance, carcass traits, meat quality, antioxidant capacity, and fatty acid composition of broilers fed corn dried distillers grains with solubles.Poult Sci. 2014 May;93(5):1202-10. doi: 10.3382/ps.2013-03683. Poult Sci. 2014. PMID: 24795313
-
Facilitating the acceptance of tangibly reduced-crude protein diets for chicken-meat production.Anim Nutr. 2020 Sep;6(3):247-257. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2020.06.001. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Anim Nutr. 2020. PMID: 33005758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutritional Strategies to Improve Meat Quality and Composition in the Challenging Conditions of Broiler Production: A Review.Animals (Basel). 2023 Apr 18;13(8):1386. doi: 10.3390/ani13081386. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37106949 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Different Forms of Butyric Acid on the Performance of Turkeys, Carcass Quality, Incidence of Footpad Dermatitis and Economic Efficiency.Animals (Basel). 2022 Jun 4;12(11):1458. doi: 10.3390/ani12111458. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35681923 Free PMC article.
-
Co-fermented yellow wine lees by Bacillus subtilis and Enterococcus faecium regulates growth performance and gut microbiota in finishing pigs.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 21;13:1003498. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1003498. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36338073 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Hepatic Insulin and Glucagon Signaling by Nutritional Factors in Broiler Chicken.Vet Sci. 2022 Feb 25;9(3):103. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9030103. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35324832 Free PMC article.
-
Butyric and Citric Acids and Their Salts in Poultry Nutrition: Effects on Gut Health and Intestinal Microbiota.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 27;22(19):10392. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910392. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary Protected Sodium Butyrate and/or Olive Leaf and Grape-Based By-Product Supplementation Modifies Productive Performance, Antioxidant Status and Meat Quality in Broilers.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jan 15;12(1):201. doi: 10.3390/antiox12010201. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36671062 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aftab U, Ashraf M, Jiang Z. Low protein diets for broilers. World Poultry Sci J. 2006;62:688–701.
-
- Aletor VA, Hamid II, Niess E, Pfeffer E. Low-protein amino acid-supplemented diets in broiler chickens: effects on performance, carcass characteristics, whole-body composition and efficiencies of nutrient utilisation. J Sci Food Agr. 2000;80:547–554.
-
- AOAC . Official Methods of Analysis. 15th Edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists; Washington, DC: 1990. pp. 1–2560.
-
- Antongiovanni M, Buccioni A, Petacchi F, Leeson S, Minieri S, Martini A, Cecchi R. Butyric acid glycerides in the diet of broiler chickens: effects on gut histology and carcass composition. Ital. J Anim Sci. 2007;6:19–25.
-
- Aviagen . Broiler Management Handbook: Ross 308. Aviagen Ltd.; Newbridge, UK: 2014. pp. 1–132.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
