Cellular senescence and chronological age in various human tissues: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 31808308
- PMCID: PMC6996941
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.13083
Cellular senescence and chronological age in various human tissues: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Senescent cells in tissues and organs are considered to be pivotal to not only the aging process but also the onset of chronic disease. Accumulating evidence from animal experiments indicates that the magnitude of senescence can vary within and between aged tissue samples from the same animal. However, whether this variation in senescence translates across to human tissue samples is unknown. To address this fundamental question, we have conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of all available literature investigating the magnitude of senescence and its association with chronological age in human tissue samples. While senescence is higher in aged tissue samples, the magnitude of senescence varies considerably depending upon tissue type, tissue section, and marker used to detect senescence. These findings echo animal experiments demonstrating that senescence levels may vary between organs within the same animal.
Keywords: aging; cell cycle proteins; cellular senescence; human; immunosenescence.
© 2019 The Authors. Aging Cell published by the Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
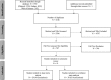
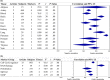

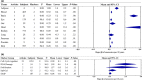
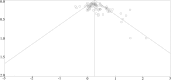
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

