A functional polymorphism rs10830963 in melatonin receptor 1B associated with the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 31808503
- PMCID: PMC6923336
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20190744
A functional polymorphism rs10830963 in melatonin receptor 1B associated with the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus
Erratum in
-
Correction: A functional polymorphism rs10830963 in melatonin receptor 1B associated with the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus.Biosci Rep. 2020 Feb 28;40(2):BSR-20190744_COR. doi: 10.1042/BSR-20190744_COR. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32109291 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
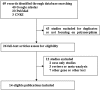
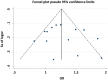
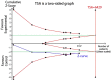
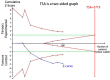
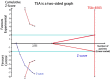
The melatonin receptor 1B (MTNR1B) polymorphism rs10830963 C>G has been reported to be associated with the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) with inconsistent results. To clarify the effect of the polymorphism on the risk of GDM, a meta-analysis therefore was performed. Pooled OR with its corresponding 95%CI was used to estimate the strength of the association. Totally 14 eligible studies with a number of 5033 GDM patients and 5614 controls were included in this meta-analysis. Results indicated that the variant G allele was significantly associated with an increased GDM risk (CG vs. CC: OR = 1.25, 95% CI = 1.11-1.40, P < 0.001; GG vs. CC: OR = 1.78, 95% CI = 1.45-2.19, P < 0.001; G vs. C: OR = 1.33, 95% CI = 1.21-1.47, P < 0.001). In the stratified analysis by ethnicity, similar results were found in Asians (CG vs. CC: OR = 1.15, 95%CI = 1.02-1.28, P = 0.020; GG vs. CC: OR = 1.52, 95% CI = 1.23-1.89, P < 0.001; G vs. C: OR = 1.23, 95% CI = 1.10-1.37, P < 0.001) and in Caucasians (CG vs. CC: OR = 1.40, 95% CI = 1.16-1.70, P < 0.001; GG vs. CC: OR = 2.21, 95% CI = 1.54-3.17, P < 0.001; G vs. C: OR = 1.47, 95% CI = 1.24-1.73, P < 0.001). FPRP and TSA analyses confirmed findings support that the rs10830963 G allele increases the risk of GDM, and further functional experimental studies are warranted to explore and clarify the potential mechanism.
Keywords: Gestational diabetes mellitus; MTNR1B; Polymorphism; Trial sequential analysis; meta analysis.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures







Comment in
-
Comments on: A functional polymorphism rs10830963 in melatonin receptor 1B associated with the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus.Biosci Rep. 2020 Feb 28;40(2):BSR20194316. doi: 10.1042/BSR20194316. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32022227 Free PMC article.
-
Reply to Comments on 'A functional polymorphism rs10830963 in melatonin receptor 1B associated with the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus'.Biosci Rep. 2020 Feb 28;40(2):BSR20200370. doi: 10.1042/BSR20200370. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32109292 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
The roles of ADIPOQ rs266729 and MTNR1B rs10830963 polymorphisms in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis.Gene. 2020 Mar 10;730:144302. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.144302. Epub 2019 Dec 26. Gene. 2020. PMID: 31884106 Review.
-
MTNR1A and MTNR1B gene polymorphisms in women with gestational diabetes.Gynecol Endocrinol. 2017 May;33(5):395-398. doi: 10.1080/09513590.2016.1276556. Epub 2017 Jan 13. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28084098
-
Association Between a Melatonin Receptor 1B Genetic Polymorphism and Its Protein Expression in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.Reprod Sci. 2019 Oct;26(10):1382-1388. doi: 10.1177/1933719118765983. Epub 2018 Apr 16. Reprod Sci. 2019. PMID: 29656698
-
Relationship between melatonin receptor 1B (rs10830963 and rs1387153) with gestational diabetes mellitus: a case-control study and meta-analysis.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2016 Jul;294(1):55-61. doi: 10.1007/s00404-015-3948-y. Epub 2015 Nov 12. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2016. PMID: 26563312
-
The polymorphisms of melatonin receptor 1B gene (MTNR1B) (rs4753426 and rs10830963) and susceptibility to adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a meta-analysis.J Orthop Sci. 2015 Jul;20(4):593-600. doi: 10.1007/s00776-015-0725-5. Epub 2015 Apr 22. J Orthop Sci. 2015. PMID: 25898821 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-blood type O is associated with an increased likelihood of gestational diabetes development: findings from an updated meta-analysis.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025 May 30;24(1):133. doi: 10.1007/s40200-025-01653-1. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025. PMID: 40454182 Review.
-
Susceptibility loci identified in Han Chinese influence genetic predisposition of PCOS in Indian women.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Jan 22;51(1):160. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-09004-0. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38252377
-
Molecular Mechanisms of the Melatonin Receptor Pathway Linking Circadian Rhythm to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 15;15(6):1406. doi: 10.3390/nu15061406. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36986139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comments on: A functional polymorphism rs10830963 in melatonin receptor 1B associated with the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus.Biosci Rep. 2020 Feb 28;40(2):BSR20194316. doi: 10.1042/BSR20194316. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32022227 Free PMC article.
-
Chronological Age Interacts with the Circadian Melatonin Receptor 1B Gene Variation, Determining Fasting Glucose Concentrations in Mediterranean Populations. Additional Analyses on Type-2 Diabetes Risk.Nutrients. 2020 Oct 29;12(11):3323. doi: 10.3390/nu12113323. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33138317 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

