Transforming growth factor-β1-regulated Fas/FasL pathway activation suppresses nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis in an inflammatory environment
- PMID: 31808511
- PMCID: PMC7005578
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20191726
Transforming growth factor-β1-regulated Fas/FasL pathway activation suppresses nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis in an inflammatory environment
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Transforming growth factor-β1-regulated Fas/FasL pathway activation suppresses nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis in an inflammatory environment.Biosci Rep. 2024 Aug 28;44(8):BSR-2019-1726_RET. doi: 10.1042/BSR-2019-1726_RET. Biosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39171797 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: During disc degeneration, inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α is correlated with nucleus pulposus (NP) cell apoptosis. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 has the potential to regenerate degenerative disc.
Objective: To investigate the protective role of TGF-β1 against TNF-α-mediated NP cell apoptosis and the underlying mechanism.
Methods: Rat NP cells were treated with TNF-α (100 ng/ml) for 48 h. TGF-β1 was added into the culture medium to investigate its protective effects against TNF-α-induced NP cell apoptosis. Exogenous FasL was used to investigate the potential role of the Fas/FasL pathway in this process. Flow cytometry assay was used to analyze NP cell apoptosis. Real-time PCR and Western blotting were used to analyze gene and protein expression of apoptosis-related molecules.
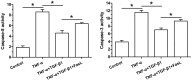
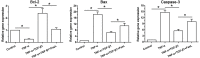
Results: In TNF-α-treated NP cells, TGF-β1 significantly decreased NP cell apoptosis, declined caspase-3 and -8 activity, and decreased expression of Bax and caspase-3 (cleaved-caspase-3) but increased expression of Bcl-2. However, exogenous FasL partly reversed these effects of TGF-β1 in NP cells treated with TNF-α. Additionally, expression of Fas and FasL in TNF-α-treated NP cells partly decreased by TGF-β1, whereas exogenous FasL increased expression of Fas and FasL in NP cells treated with TGF-β1 and TNF-α.
Conclusion: TGF-β1 helps to inhibit TNF-α-induced NP cell apoptosis and the Fas/FasL pathway may be involved in this process. The present study suggests that TGF-β1 may be effective to retard inflammation-mediated disc degeneration.
Keywords: Fas/FasL; TGF-β1; TNF-α; apoptosis; nucleus pulposus.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
All animal experiments in the present study were performed in the Central Laboratory of Xinhua Hospital, and the animal tissue separation procedure was approved by the Ethics Committee at Xinhua Hospital affiliated to Medical School of Shanghai Jiaotong Universtiy [SHU(W) 2015-1202].
Figures



Similar articles
-
Lysyl oxidase inhibits TNF-α induced rat nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis via regulating Fas/FasL pathway and the p53 pathways.Life Sci. 2020 Nov 1;260:118483. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118483. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32979358
-
Osteogenic protein-1 inhibits nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis through regulating the NF-κB/ROS pathway in an inflammation environment.Biosci Rep. 2018 Nov 20;38(6):BSR20181530. doi: 10.1042/BSR20181530. Print 2018 Dec 21. Biosci Rep. 2018. Retraction in: Biosci Rep. 2024 Aug 28;44(8):BSR-2018-1530_RET. doi: 10.1042/BSR-2018-1530_RET. PMID: 30341245 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Mechano growth factor attenuates mechanical overload-induced nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis through inhibiting the p38 MAPK pathway.Biosci Rep. 2019 Mar 28;39(3):BSR20182462. doi: 10.1042/BSR20182462. Print 2019 Mar 29. Biosci Rep. 2019. Retraction in: Biosci Rep. 2024 Aug 28;44(8):BSR-2018-2462_RET. doi: 10.1042/BSR-2018-2462_RET. PMID: 30858307 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The role of the Fas/FasL signaling pathway in environmental toxicant-induced testicular cell apoptosis: An update.Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2018 Apr;64(2):93-102. doi: 10.1080/19396368.2017.1422046. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2018. PMID: 29299971 Review.
-
Many checkpoints on the road to cell death: regulation of Fas-FasL interactions and Fas signaling in peripheral immune responses.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2009;49:17-47. doi: 10.1007/400_2008_24. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2009. PMID: 19132321 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Subversive molecular role of Krüppel-like factor 5 in extracellular matrix degradation and chondrocyte dedifferentiation.Funct Integr Genomics. 2022 Dec;22(6):1307-1313. doi: 10.1007/s10142-022-00892-2. Epub 2022 Aug 5. Funct Integr Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35931836
-
Role of Caspase Family in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration and Its Therapeutic Prospects.Biomolecules. 2022 Aug 4;12(8):1074. doi: 10.3390/biom12081074. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36008968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulated cell death: Implications for intervertebral disc degeneration and therapy.J Orthop Translat. 2022 Nov 5;37:163-172. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2022.10.009. eCollection 2022 Nov. J Orthop Translat. 2022. PMID: 36380883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-endothelial cell antibodies in pathogenesis of vasculitis.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 30;16:1567293. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1567293. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40370444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Codelivery of TGF-β1 and anti-miR-141 by PLGA microspheres inhibits progression of intervertebral disc degeneration.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Jan 6;18(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03501-5. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 36609253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Macfarlane G.J., Thomas E., Croft P.R., Papageorgiou A.C., Jayson M.I. and Silman A.J. (1999) Predictors of early improvement in low back pain amongst consulters to general practice: the influence of pre-morbid and episode-related factors. Pain 80, 113–119 10.1016/S0304-3959(98)00209-7 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

