Idiopathic aplastic anemia vs hypocellular myelodysplastic syndrome
- PMID: 31808900
- PMCID: PMC6913491
- DOI: 10.1182/hematology.2019000019
Idiopathic aplastic anemia vs hypocellular myelodysplastic syndrome
Abstract
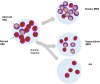
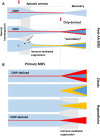
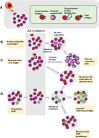
Proper diagnostic distinction of bone marrow failure syndromes can often be challenging. In particular, for older patients with idiopathic aplastic anemia (AA), differential diagnosis includes myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), which can atypically present in a hypocellular form. In addition to blasts and overt dysplasia, the presence of chromosomal abnormalities and a spectrum of somatic mutations may be revealing. Both clonal cytogenetic aberrations and somatic mutations most typically correspond to a clonal myelodysplasia, but clonal somatic mutations have also recently been found in AA. True driver myeloid mutations are uncommon in AA. Marrow hypocellularity in AA and occasionally in MDS patients points toward a similar immune mechanism responsible for deficient blood cell production and indicates that cytopenias in early hypocellular MDS might be treated with immunosuppressive modalities. Primary hypocellular MDS has to be distinguished from post-AA secondary MDS, most commonly associated with del7/7q. Post-AA MDS evolves at the rate of about 10% in 10 years, but recent observations suggest that widespread use of eltrombopag may influence the risk of progression to MDS. This complication likely represents a clonal escape, with founder hits occurring early on in the course of AA. A similar mechanism operates in the evolution of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) in AA patients, but PNH clones are rarely encountered in primary MDS.
© 2019 by The American Society of Hematology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: J.D. and J.P.M. declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evolution of clonal cytogenetic abnormalities in aplastic anemia.Leuk Lymphoma. 2004 Mar;45(3):433-40. doi: 10.1080/10428190310001602363. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004. PMID: 15160903 Review.
-
Secondary myelodysplastic syndrome and leukemia in acquired aplastic anemia and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria.Blood. 2020 Jul 2;136(1):36-49. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000940. Blood. 2020. PMID: 32430502 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and prognostic significance of small paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria clones in myelodysplastic syndrome and aplastic anemia.Leukemia. 2021 Nov;35(11):3223-3231. doi: 10.1038/s41375-021-01190-9. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Leukemia. 2021. PMID: 33664463 Free PMC article.
-
N-RAS gene mutation in patients with aplastic anemia and aplastic anemia/ paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria during evolution to clonal disease.Blood. 2000 Jan 15;95(2):646-50. Blood. 2000. PMID: 10627475
-
Myelodysplastic syndrome and aplastic anemia: distinct entities or diseases linked by a common pathophysiology?Semin Hematol. 2000 Jan;37(1):15-29. doi: 10.1016/s0037-1963(00)90027-1. Semin Hematol. 2000. PMID: 10676908 Review.
Cited by
-
Whole Exome Sequencing of Adult Indians with Apparently Acquired Aplastic Anaemia: Initial Experience at Tertiary Care Hospital.Diseases. 2024 Sep 23;12(9):225. doi: 10.3390/diseases12090225. Diseases. 2024. PMID: 39329894 Free PMC article.
-
Novel therapeutic choices in immune aplastic anemia.F1000Res. 2020 Sep 10;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-1118. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.22214.1. eCollection 2020. F1000Res. 2020. PMID: 32953089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoplastic myelodysplastic syndrome and acquired aplastic anemia: Immune‑mediated bone marrow failure syndromes (Review).Int J Oncol. 2022 Jan;60(1):7. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5297. Epub 2021 Dec 27. Int J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34958107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aplastic Anemia in Triple X Syndrome.Children (Basel). 2023 Jan 3;10(1):100. doi: 10.3390/children10010100. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36670650 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement for the Area of Red Blood Cells From Microscopic Images Based on Image Processing Technology and Its Applications in Aplastic Anemia, Megaloblastic Anemia, and Myelodysplastic Syndrome.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jan 25;8:796920. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.796920. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35145978 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bono E, McLornan D, Travaglino E, et al. . Clinical, histopathological and molecular characterization of hypoplastic myelodysplastic syndrome [published online ahead of print 2 April 2019]. Leukemia. doi:10.1038/s41375-019-0457-1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

