The regulatory protein 14-3-3β binds to the IQ motifs of myosin-IC independent of phosphorylation
- PMID: 31811090
- PMCID: PMC7086031
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011227
The regulatory protein 14-3-3β binds to the IQ motifs of myosin-IC independent of phosphorylation
Abstract
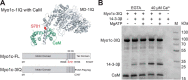
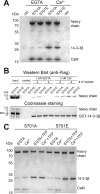
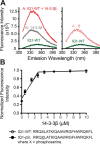
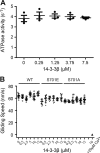
Myosin-IC (Myo1c) has been proposed to function in delivery of glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4)-containing vesicles to the plasma membrane in response to insulin stimulation. Current evidence suggests that, upon insulin stimulation, Myo1c is phosphorylated at Ser701, leading to binding of the signaling protein 14-3-3β. Biochemical and functional details of the Myo1c-14-3-3β interaction have yet to be described. Using recombinantly expressed proteins and mass spectrometry-based analyses to monitor Myo1c phosphorylation, along with pulldown, fluorescence binding, and additional biochemical assays, we show here that 14-3-3β is a dimer and, consistent with previous work, that it binds to Myo1c in the presence of calcium. This interaction was associated with dissociation of calmodulin (CaM) from the IQ motif in Myo1c. Surprisingly, we found that 14-3-3β binds to Myo1c independent of Ser701 phosphorylation in vitro Additionally, in contrast to previous reports, we did not observe Myo1c Ser701 phosphorylation by Ca2+/CaM-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), although CaMKII phosphorylated four other Myo1c sites. The presence of 14-3-3β had little effect on the actin-activated ATPase or motile activities of Myo1c. Given these results, it is unlikely that 14-3-3β acts as a cargo adaptor for Myo1c-powered transport; rather, we propose that 14-3-3β binds Myo1c in the presence of calcium and stabilizes the calmodulin-dissociated, nonmotile myosin.
Keywords: 14-3-3 protein; 14-3-3β; calmodulin (CaM); cell motility; cell signaling; cytoskeleton; molecular motor; myo1c; myosin; myosin-IC.
© 2020 Ji and Ostap.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health
Figures

Comment in
-
Putting the brakes on a myosin motor.J Biol Chem. 2020 Mar 20;295(12):3757-3758. doi: 10.1074/jbc.H120.013153. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32198186 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

