Low diagnostic accuracy of Xpert MTB/RIF assay for extrapulmonary tuberculosis: A multicenter surveillance
- PMID: 31811239
- PMCID: PMC6898377
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-55112-y
Low diagnostic accuracy of Xpert MTB/RIF assay for extrapulmonary tuberculosis: A multicenter surveillance
Abstract
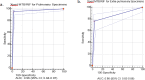
Diagnostic accuracy of Xpert MTB/RIF assay for pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) and extrapulmonary TB (EPTB) has not been investigated in Iran. This study was aimed to assess the diagnostic accuracy of Xpert MTB/RIF assay for both PTB and EPTB. A total of 2111 clinical samples (1218 pulmonary and 838 extra-pulmonary) were collected from 16 medical centers during the study period and were analyzed for detection of PTB and EPTB by both Xpert MTB/RIF assay and standard conventional methods (culture and direct smear microscopy). The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) of Xpert MTB/RIF assay for PTB were found to be 95.5%, 96.7%, 83.8%, and 99.1% respectively. For EPTB, the sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV of Xpert MTB/RIF assay counted for 76.5%, 95.9%, 62%, and 97.9% respectively. Xpert MTB/RIF assay found to be highly sensitive, specific and comparable to standard conventional methods for the diagnosis of PTB. However, the sensitivity and specificity of Xpert MTB/RIF for EPTB specimens were highly variable; thus, Xpert MTB/RIF cannot be recommended to replace standard conventional tests for diagnosis of EPTB.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global tuberculosis report (2017).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

