iRGD-guided tamoxifen polymersomes inhibit estrogen receptor transcriptional activity and decrease the number of breast cancer cells with self-renewing capacity
- PMID: 31812165
- PMCID: PMC6898937
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-019-0553-4
iRGD-guided tamoxifen polymersomes inhibit estrogen receptor transcriptional activity and decrease the number of breast cancer cells with self-renewing capacity
Abstract
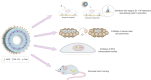
Background: Tamoxifen (Tam) is the most frequent treatment for estrogen receptor (ER) positive breast cancer. We recently showed that fibronectin (FN) leads to Tam resistance and selection of breast cancer stem cells. With the aim of developing a nanoformulation that would simultaneously tackle ER and FN/β1 integrin interactions, we designed polyethylene glycol-polycaprolactone polymersomes polymersomes (PS) that carry Tam and are functionalized with the tumor-penetrating iRGD peptide (iRGD-PS-Tam).
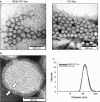
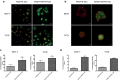
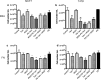
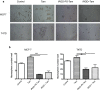
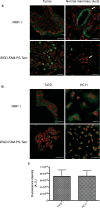
Results: Polyethylene glycol-polycaprolactone PS were assembled and loaded with Tam using the hydration film method. The loading of encapsulated Tam, measured by UPLC, was 2.4 ± 0.5 mol Tam/mol polymer. Physicochemical characterization of the PS demonstrated that iRGD functionalization had no effect on morphology, and a minimal effect on the PS size and polydispersity (176 nm and Pdi 0.37 for iRGD-TAM-PS and 171 nm and Pdi 0.36 for TAM-PS). iRGD-PS-Tam were taken up by ER+ breast carcinoma cells in 2D-culture and exhibited increased penetration of 3D-spheroids. Treatment with iRGD-PS-Tam inhibited proliferation and sensitized cells cultured on FN to Tam. Mechanistically, treatment with iRGD-PS-Tam resulted in inhibition ER transcriptional activity as evaluated by a luciferase reporter assay. iRGD-PS-Tam reduced the number of cells with self-renewing capacity, a characteristic of breast cancer stem cells. In vivo, systemic iRGD-PS-Tam showed selective accumulation at the tumor site.
Conclusions: Our study suggests iRGD-guided delivery of PS-Tam as a potential novel therapeutic strategy for the management of breast tumors that express high levels of FN. Future studies in pre-clinical in vivo models are warranted.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Endocrine resistance; Fibronectin; Self-renewing capacity; Tamoxifen; iRGD-guided polymersomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
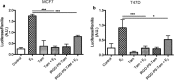

Similar articles
-
ERK/MAPK regulates ERRγ expression, transcriptional activity and receptor-mediated tamoxifen resistance in ER+ breast cancer.FEBS J. 2014 May;281(10):2431-42. doi: 10.1111/febs.12797. Epub 2014 Apr 28. FEBS J. 2014. PMID: 24684682 Free PMC article.
-
Keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) induces tamoxifen (Tam) resistance in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells.Anticancer Res. 2006 May-Jun;26(3A):1773-84. Anticancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16827106
-
Estrogen receptor-α36 is involved in development of acquired tamoxifen resistance via regulating the growth status switch in breast cancer cells.Mol Oncol. 2013 Jun;7(3):611-24. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2013.02.001. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Mol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23499324 Free PMC article.
-
[Cytotoxicity of tamoxifen and its principal metabolites in human breast cancer cell lines].Bull Cancer. 1996 Oct;83(10):808-15. Bull Cancer. 1996. PMID: 8952630 Review. French.
-
Novel Tamoxifen Nanoformulations for Improving Breast Cancer Treatment: Old Wine in New Bottles.Molecules. 2020 Mar 5;25(5):1182. doi: 10.3390/molecules25051182. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32151063 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pro-Tumorigenic Macrophage Infiltration in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Possible Macrophage-Aimed Therapeutic Interventions.Front Oncol. 2021 May 10;11:675664. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.675664. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34041037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modified Bovine Milk Exosomes for Doxorubicin Delivery to Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2022 May 16;5(5):2163-2175. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.2c00015. Epub 2022 Apr 13. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2022. PMID: 35417133 Free PMC article.
-
iRGD Peptide as a Tumor-Penetrating Enhancer for Tumor-Targeted Drug Delivery.Polymers (Basel). 2020 Aug 24;12(9):1906. doi: 10.3390/polym12091906. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32847045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular Endothelial Cells: Heterogeneity and Targeting Approaches.Cells. 2021 Oct 10;10(10):2712. doi: 10.3390/cells10102712. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymersomes as Innovative, Stimuli-Responsive Platforms for Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Mar 26;16(4):463. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16040463. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38675124 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Davies C, Pan H, Godwin J, Gray R, Arriagada R, Raina V, et al. Long-term effects of continuing adjuvant tamoxifen to 10 years versus stopping at 5 years after diagnosis of oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: ATLAS, a randomised trial. Lancet. 2013;381(9869):805–816. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61963-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

