Estimates of incidence and mortality of cervical cancer in 2018: a worldwide analysis
- PMID: 31812369
- PMCID: PMC7025157
- DOI: 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30482-6
Estimates of incidence and mortality of cervical cancer in 2018: a worldwide analysis
Erratum in
-
Correction to Lancet Glob Health 2020; 8: e191-203.Lancet Glob Health. 2022 Jan;10(1):e41. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00554-4. Lancet Glob Health. 2022. PMID: 34919855 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The knowledge that persistent human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is the main cause of cervical cancer has resulted in the development of prophylactic vaccines to prevent HPV infection and HPV assays that detect nucleic acids of the virus. WHO has launched a Global Initiative to scale up preventive, screening, and treatment interventions to eliminate cervical cancer as a public health problem during the 21st century. Therefore, our study aimed to assess the existing burden of cervical cancer as a baseline from which to assess the effect of this initiative.
Methods: For this worldwide analysis, we used data of cancer estimates from 185 countries from the Global Cancer Observatory 2018 database. We used a hierarchy of methods dependent on the availability and quality of the source information from population-based cancer registries to estimate incidence of cervical cancer. For estimation of cervical cancer mortality, we used the WHO mortality database. Countries were grouped in 21 subcontinents and were also categorised as high-resource or lower-resource countries, on the basis of their Human Development Index. We calculated the number of cervical cancer cases and deaths in a given country, directly age-standardised incidence and mortality rate of cervical cancer, indirectly standardised incidence ratio and mortality ratio, cumulative incidence and mortality rate, and average age at diagnosis.
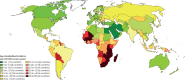
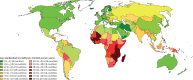
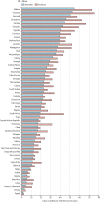
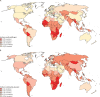
Findings: Approximately 570 000 cases of cervical cancer and 311 000 deaths from the disease occurred in 2018. Cervical cancer was the fourth most common cancer in women, ranking after breast cancer (2·1 million cases), colorectal cancer (0·8 million) and lung cancer (0·7 million). The estimated age-standardised incidence of cervical cancer was 13·1 per 100 000 women globally and varied widely among countries, with rates ranging from less than 2 to 75 per 100 000 women. Cervical cancer was the leading cause of cancer-related death in women in eastern, western, middle, and southern Africa. The highest incidence was estimated in Eswatini, with approximately 6·5% of women developing cervical cancer before age 75 years. China and India together contributed more than a third of the global cervical burden, with 106 000 cases in China and 97 000 cases in India, and 48 000 deaths in China and 60 000 deaths in India. Globally, the average age at diagnosis of cervical cancer was 53 years, ranging from 44 years (Vanuatu) to 68 years (Singapore). The global average age at death from cervical cancer was 59 years, ranging from 45 years (Vanuatu) to 76 years (Martinique). Cervical cancer ranked in the top three cancers affecting women younger than 45 years in 146 (79%) of 185 countries assessed.
Interpretation: Cervical cancer continues to be a major public health problem affecting middle-aged women, particularly in less-resourced countries. The global scale-up of HPV vaccination and HPV-based screening-including self-sampling-has potential to make cervical cancer a rare disease in the decades to come. Our study could help shape and monitor the initiative to eliminate cervical cancer as a major public health problem.
Funding: Belgian Foundation Against Cancer, DG Research and Innovation of the European Commission, and The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Impact of scaled up human papillomavirus vaccination and cervical screening and the potential for global elimination of cervical cancer in 181 countries, 2020-99: a modelling study.Lancet Oncol. 2019 Mar;20(3):394-407. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30836-2. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Lancet Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30795950
-
Worldwide burden of cervical cancer in 2008.Ann Oncol. 2011 Dec;22(12):2675-2686. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdr015. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Ann Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21471563
-
Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016.Lancet. 2017 Sep 16;390(10100):1151-1210. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32152-9. Lancet. 2017. PMID: 28919116 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional, and national burden of respiratory tract cancers and associated risk factors from 1990 to 2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.Lancet Respir Med. 2021 Sep;9(9):1030-1049. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00164-8. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Lancet Respir Med. 2021. PMID: 34411511 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Early adoption of innovation in HPV prevention strategies: closing the gap in cervical cancer.Ecancermedicalscience. 2024 Sep 11;18:1762. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2024.1762. eCollection 2024. Ecancermedicalscience. 2024. PMID: 39430092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Locally advanced cervical cancer: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus radical surgery an alternative approach to chemo-radiation in a low-income setting: A descriptive study.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 30;19(10):e0310457. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310457. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39475968 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and inflammatory potential of diet among women at risk of cervical cancer: findings from a cross-sectional study in Italy.Public Health Nutr. 2022 Jun;25(6):1577-1585. doi: 10.1017/S1368980021001944. Epub 2021 May 7. Public Health Nutr. 2022. PMID: 33958013 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism underlying long non‑coding RNA ILF3‑AS1‑mediated inhibition of cervical cancer cell proliferation, invasion and migration, and promotion of apoptosis.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Aug;24(2):554. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12193. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34080029 Free PMC article.
-
The burden of cervical cancer in China.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 20;12:979809. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.979809. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36203427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arbyn M, Castellsagué X, de Sanjosé S. Worldwide burden of cervical cancer in 2008. Ann Oncol. 2011;22:2675–2686. - PubMed
-
- de Sanjose S, Quint WG, Alemany L. Human papillomavirus genotype attribution in invasive cervical cancer: a retrospective cross-sectional worldwide study. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:1048–1056. - PubMed
-
- Bzhalava D, Guan P, Franceschi S, Dillner J, Clifford G. A systematic review of the prevalence of mucosal and cutaneous human papillomavirus types. Virology. 2013;445:224–231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

