Real-Time Value Integration during Economic Choice Is Regulated by Orbitofrontal Cortex
- PMID: 31813612
- PMCID: PMC6917829
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.10.058
Real-Time Value Integration during Economic Choice Is Regulated by Orbitofrontal Cortex
Abstract
Neural correlates implicate the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) in value-based or economic decision making [1-3]. Yet inactivation of OFC in rats performing a rodent version of the standard economic choice task is without effect [4, 5], a finding more in accord with ideas that the OFC is primarily necessary for behavior when new information must be taken into account [6-9]. Neural activity in the OFC spontaneously updates to reflect new information, particularly about outcomes [10-16], and the OFC is necessary for adjustments to learned behavior only under these conditions [4, 16-26]. Here, we merge these two independent lines of research by inactivating lateral OFC during an economic choice that requires new information about the value of the predicted outcomes to be incorporated into an already established choice. Outcome value was changed by pre-feeding the rats one of two food options before testing. In control rats, this pre-feeding resulted in divergent changes in choice behavior that depended on the rats' prior preference for the pre-fed food. Optogenetic inactivation of the OFC disrupted this bi-directional effect of pre-feeding without affecting other measures that describe the underlying choice behavior. This finding unifies the role of the OFC in economic choice with its role in a host of other behaviors, causally demonstrating that the OFC is not necessary for economic choice per se-unless that choice incorporates new information about the outcomes.
Keywords: decision-making; economic; optogenetics; orbitofrontal; revaluation; satiety.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
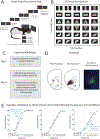
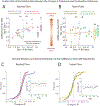
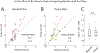

Comment in
-
Neuroscience: Reevaluating the Role of Orbitofrontal Cortex.Curr Biol. 2019 Dec 16;29(24):R1314-R1316. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2019.10.063. Curr Biol. 2019. PMID: 31846680
Similar articles
-
Medial orbitofrontal inactivation does not affect economic choice.Elife. 2018 Oct 3;7:e38963. doi: 10.7554/eLife.38963. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30281020 Free PMC article.
-
Lateral Orbitofrontal Inactivation Dissociates Devaluation-Sensitive Behavior and Economic Choice.Neuron. 2017 Dec 6;96(5):1192-1203.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.10.026. Epub 2017 Nov 16. Neuron. 2017. PMID: 29154127 Free PMC article.
-
Orbitofrontal State Representations Are Related to Choice Adaptations and Reward Predictions.J Neurosci. 2021 Mar 3;41(9):1941-1951. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0753-20.2020. Epub 2021 Jan 14. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33446521 Free PMC article.
-
Orbitofrontal cortex and the computation of economic value.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Dec;1121:232-53. doi: 10.1196/annals.1401.011. Epub 2007 Aug 14. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 17698992 Review.
-
Taking stock of value in the orbitofrontal cortex.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2022 Jul;23(7):428-438. doi: 10.1038/s41583-022-00589-2. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35468999 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neural Population Dynamics Underlying Expected Value Computation.J Neurosci. 2021 Feb 24;41(8):1684-1698. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1987-20.2020. Epub 2021 Jan 13. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33441432 Free PMC article.
-
The orbitofrontal cartographer.Behav Neurosci. 2021 Apr;135(2):267-276. doi: 10.1037/bne0000463. Behav Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34060879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dopaminergic responses to identity prediction errors depend differently on the orbitofrontal cortex and hippocampus.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 17:2024.12.11.628003. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.11.628003. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Behav Neurosci. 2025 Sep 01. doi: 10.1037/bne0000633. PMID: 39763911 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Neural mechanisms of economic choices in mice.Elife. 2020 Feb 25;9:e49669. doi: 10.7554/eLife.49669. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32096761 Free PMC article.
-
Defining an orbitofrontal compass: Functional and anatomical heterogeneity across anterior-posterior and medial-lateral axes.Behav Neurosci. 2021 Apr;135(2):165-173. doi: 10.1037/bne0000442. Behav Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34060873 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

