Usp9X Controls Ankyrin-Repeat Domain Protein Homeostasis during Dendritic Spine Development
- PMID: 31813652
- PMCID: PMC7007386
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.11.003
Usp9X Controls Ankyrin-Repeat Domain Protein Homeostasis during Dendritic Spine Development
Abstract
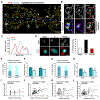
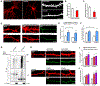
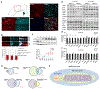
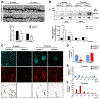
Variants in the ANK3 gene encoding ankyrin-G are associated with neurodevelopmental disorders, including intellectual disability, autism, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder. However, no upstream regulators of ankyrin-G at synapses are known. Here, we show that ankyrin-G interacts with Usp9X, a neurodevelopmental-disorder-associated deubiquitinase (DUB). Usp9X phosphorylation enhances their interaction, decreases ankyrin-G polyubiquitination, and stabilizes ankyrin-G to maintain dendritic spine development. In forebrain-specific Usp9X knockout mice (Usp9X-/Y), ankyrin-G as well as multiple ankyrin-repeat domain (ANKRD)-containing proteins are transiently reduced at 2 but recovered at 12 weeks postnatally. However, reduced cortical spine density in knockouts persists into adulthood. Usp9X-/Y mice display increase of ankyrin-G ubiquitination and aggregation and hyperactivity. USP9X mutations in patients with intellectual disability and autism ablate its catalytic activity or ankyrin-G interaction. Our data reveal a DUB-dependent mechanism of ANKRD protein homeostasis, the impairment of which only transiently affects ANKRD protein levels but leads to persistent neuronal, behavioral, and clinical abnormalities.
Keywords: ANK; SHANK; ankyrin-G; deubiquitinase; intellectual disability; proximity ligation assay; structured illumination microscopy.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Al-Hakim AK, Zagorska A, Chapman L, Deak M, Peggie M, and Alessi DR (2008). Control of AMPK-related kinases by USP9X and atypical Lys(29)/Lys(33)-linked polyubiquitin chains. Biochem J 411, 249–260. - PubMed
-
- Amerik AY, and Hochstrasser M (2004). Mechanism and function of deubiquitinating enzymes. Bba-Mol Cell Res 1695, 189–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

