The global burden of neurological disorders: translating evidence into policy
- PMID: 31813850
- PMCID: PMC9945815
- DOI: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30411-9
The global burden of neurological disorders: translating evidence into policy
Abstract
Neurological disorders are the leading cause of disability and the second leading cause of death worldwide. In the past 30 years, the absolute numbers of deaths and people with disabilities owing to neurological diseases have risen substantially, particularly in low-income and middle-income countries, and further increases are expected globally as a result of population growth and ageing. This rise in absolute numbers of people affected suggests that advances in prevention and management of major neurological disorders are not sufficiently effective to counter global demographic changes. Urgent measures to reduce this burden are therefore needed. Because resources for health care and research are already overstretched, priorities need to be set to guide policy makers, governments, and funding organisations to develop and implement action plans for prevention, health care, and research to tackle the growing challenge of neurological disorders.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests
VLF reports that he is a CEO of the New Zealand Stroke Education (charitable) Trust, outside the submitted work. GD has served as a consultant for Boston Scientific, Cavion, and Functional Neuromodulation; has received lecture fees from Boston Scientific and royalties from Thieme publishers; and is a government employee and receives funding for his research through his institution from the German Research Council, the German Ministry of Education and Research, and Medtronic, outside the submitted work. WMC reports travel fees from Sanofi Genzyme, Biogen, and Merck, and travel and personal fees from Roche and Novartis, outside the submitted work. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
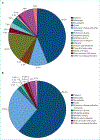
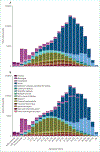
Comment in
-
The growing burden of neurological disorders in low-income and middle-income countries: priorities for policy making.Lancet Neurol. 2020 Mar;19(3):200-202. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30476-4. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Lancet Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31813849 No abstract available.
References
-
- Feigin VL, Vos T. Global burden of neurological disorders: from Global burden of disease estimates to actions. Neuroepidemiology 2019; 52: 1–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

