Cloacal malformation in a 5-month-old male dog
- PMID: 31814634
- PMCID: PMC6855225
Cloacal malformation in a 5-month-old male dog
Abstract
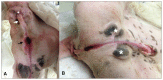
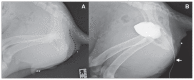
A case of a developmental cloacal anomaly is described in a 5-month-old male puppy. The animal had a unique combination of anomalies: confluence of the urethra and rectum into a common tract with a single perineal opening, atresia ani, and 3 genital anomalies, namely, a perineal hypospadias, penile hypoplasia with ventroflexural curvature, and a scrotal cleft. Surgical correction was successful, with fecal continence maintained and no urinary tract infections occurring during long-term follow-up.
Malformation cloacale chez un chiot mâle âgé de cinq mois. Un cas de développement cloacal anormal est décrit chez un chiot mâle âgé de cinq mois. L’animal avait une combinaison unique d’anomalies : une confluence de l’urètre et du rectum dans un tractus commun avec une ouverture périnéale unique, une atrésie de l’anus, et trois anomalies génitales, à savoir, un hypospadias périnéal, une hypoplasie pénienne avec courbure ventroflexurale, et une fissure scrotale. La correction chirurgicale fut une réussite, avec la continence fécale maintenue et aucune infection du tractus urinaire se produisant durant le suivi à long terme.(Traduit par Dr Serge Messier).
Copyright and/or publishing rights held by the Canadian Veterinary Medical Association.
Figures

References
-
- Cashmore RG, Ladlow JF. Creation of a urethral conduit from a preputial indirect flap in a dog with perineal hypospadias. Vet Surg. 2010;39:14–20. - PubMed
-
- Bae SW, Chung DJ, Chung WH, Park NW, Lim CY, Kim HY. A rare case of a complex of multiple congenital anomalies diagnosed using computed tomography in a male puppy. Vet Med (Praha) 2018;63:50–53.
-
- Banu T, Chowdhury TK, Hoque M, Rahman MA. Cloacal malformation variants in male. Pediatr Surg Int. 2013;29:677–682. - PubMed
-
- Pieri NCG, Souza AF, Casals JB, Roballo K, Ambrósio CE, Martins DS. Comparative development of embryonic age by organogenesis in domestic dogs and cats. Reprod Dom Anim. 2015;50:625–631. - PubMed
-
- Prassinos NN, Papazoglou LG, Adamama-Moraitou KK, Galatos AD, Gouletsou P, Rallis TS. Congenital anorectal abnormalities in six dogs. Vet Rec. 2003;153:81–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
