The Impact Of Pelvic Floor Muscle Training On Urinary Incontinence In Men After Radical Prostatectomy (RP) - A Systematic Review
- PMID: 31814714
- PMCID: PMC6858802
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S228222
The Impact Of Pelvic Floor Muscle Training On Urinary Incontinence In Men After Radical Prostatectomy (RP) - A Systematic Review
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to determine the efficacy of pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) in the treatment of urinary incontinence (UI) in men after radical prostatectomy (RP).
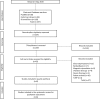
Methods: PubMed, ScienceDirect, and Cochrane Library databases were searched for studies published in years 2000-2019. We included randomized controlled trials in English which compare clinic-based vs home-based PFMT, preoperative and postoperative PFMT, supervised vs unsupervised PFMT, and PFMT alone vs no treatment at all.
Results: Eight articles were included in the final review. There was a total of 1078 patients aged 45-75 in all study groups. The study participants received radical retropubic prostatectomy or radical prostatectomy. Included studies assessed the following interventions: preoperative and postoperative PFMT, supervised vs home-based PFMT, unsupervised PFMT vs no treatment at all, and PFMT combined with resistance and flexibility exercises vs PFMT alone.
Conclusion: PFMT is an effective treatment for urinary incontinence in men after radical prostatectomy. PFMT improves not only physical parameters but also the quality of life of men after RP.
Keywords: pelvic floor muscle training; prostatectomy; urinary incontinence.
© 2019 Strączyńska et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- EAU Guidelines. Edn. presented at the EAU Annual Congress Barcelona Barcelona, Spain 2019.
-
- Schröder A, Abrams P, Andersson KE, et al. EAU guidelines on urinary incontinence. European Association of Urology 2010. Available from: http://www.uroweb.org/guidelines/online-guidelines/ Accessed October29, 2019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical