Cisplatin induces calcium ion accumulation and hearing loss by causing functional alterations in calcium channels and exocytosis
- PMID: 31814894
- PMCID: PMC6895503
Cisplatin induces calcium ion accumulation and hearing loss by causing functional alterations in calcium channels and exocytosis
Abstract
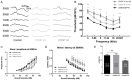
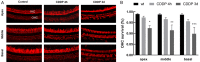
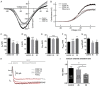
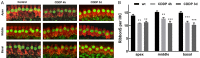
In recent years, molecular biology and biochemistry have been a focus of studies on the ototoxic side effects of cisplatin. In this paper, the application of cisplatin for 4 h and 72 h was studied from the perspective of electrophysiological function. Patch clamp experiments and immunofluorescence staining were performed on inner hair cells of the cochlea. The patch-clamp results showed that the calcium current amplitude decreased significantly at 4 h and 72 h after cisplatin treatment, the reversal potential was negatively polarized, and the activation time decreased. We suspected that intracellular calcium accumulation was responsible for this result and confirmed this hypothesis by using calpain to measure intracellular calcium concentrations. We tested membrane capacitive function, whose levels after cisplatin application were significantly lower than those in the control group, thus indicating dysfunctional cytoplasmic effervescent function. CtBP2 staining was used to verify this result and indicated a decrease in ribbon synapses. Simultaneously, we observed dysfunction of vesicle circulation after cisplatin application. We found that cisplatin induces the accumulation of calcium ions in inner hair cells by calpain staining and fluoresce intensity calculation, thus decreasing calcium current and synaptic vesicle release, and impairing vesicles cycling, all of which are important mechanisms of cisplatin-induced hearing loss.
Keywords: Cisplatin; calcium ions; exocytosis; inner hair cell; ototoxicity; ribbon synapse.
AJTR Copyright © 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Functional alteration of ribbon synapses in inner hair cells by noise exposure causing hidden hearing loss.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Aug 10;707:134268. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2019.05.022. Epub 2019 May 16. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 31103727
-
Actin Filaments Regulate Exocytosis at the Hair Cell Ribbon Synapse.J Neurosci. 2016 Jan 20;36(3):649-54. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3379-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26791198 Free PMC article.
-
Viral Transfer of Mini-Otoferlins Partially Restores the Fast Component of Exocytosis and Uncovers Ultrafast Endocytosis in Auditory Hair Cells of Otoferlin Knock-Out Mice.J Neurosci. 2019 May 1;39(18):3394-3411. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1550-18.2018. Epub 2019 Mar 4. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30833506 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that rapid vesicle replenishment of the synaptic ribbon mediates recovery from short-term adaptation at the hair cell afferent synapse.J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2004 Dec;5(4):376-90. doi: 10.1007/s10162-004-5003-8. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2004. PMID: 15675002 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms underlying the temporal precision of sound coding at the inner hair cell ribbon synapse.J Physiol. 2006 Oct 1;576(Pt 1):55-62. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.114835. Epub 2006 Aug 10. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16901948 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Macrophage Depletion Protects Against Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity and Nephrotoxicity.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 17:2023.11.16.567274. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.16.567274. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Sci Adv. 2024 Jul 26;10(30):eadk9878. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adk9878. PMID: 38014097 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Long-term auditory follow-up in the management of pediatric platinum-induced ototoxicity.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 Oct;279(10):4677-4686. doi: 10.1007/s00405-021-07225-2. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 35024956
-
Experimental animal models of drug-induced sensorineural hearing loss: a narrative review.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Sep;9(17):1393. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-2508. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34733945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protection of Cochlear Ribbon Synapses and Prevention of Hidden Hearing Loss.Neural Plast. 2020 Nov 1;2020:8815990. doi: 10.1155/2020/8815990. eCollection 2020. Neural Plast. 2020. PMID: 33204247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bile Acid Application in Cell-Targeting for Molecular Receptors in Relation to Hearing: A Comprehensive Review.Curr Drug Targets. 2024;25(3):158-170. doi: 10.2174/0113894501278292231223035733. Curr Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38192136 Review.
References
-
- Waissbluth S, Daniel SJ. Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: transporters playing a role in cisplatin toxicity. Hear Res. 2013;299:37–45. - PubMed
-
- Lu J, Liu H, Lin S, Li C, Wu H. Electrophysiological characterization of acutely isolated spiral ganglion neurons in neonatal and mature sonic hedgehog knock-in mice. Neurosci Lett. 2019;714:134536. - PubMed
-
- Wu X, Li X, Song Y, Li H, Bai X, Liu W, Han Y, Xu L, Li J, Zhang D, Wang H, Fan Z. Allicin protects auditory hair cells and spiral ganglion neurons from cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Neuropharmacology. 2017;116:429–440. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
