Akt inhibition at the initial stage of CAR-T preparation enhances the CAR-positive expression rate, memory phenotype and in vivo efficacy
- PMID: 31815041
- PMCID: PMC6895454
Akt inhibition at the initial stage of CAR-T preparation enhances the CAR-positive expression rate, memory phenotype and in vivo efficacy
Abstract
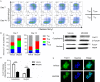
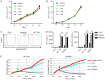
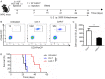
The adoptive transfer of chimeric antigen receptor-modified T (CAR-T) cells is a novel cancer treatment that has led to encouraging breakthroughs in the treatment of haematological malignancies. The efficacy of infused CAR-T cells is associated with a high CAR-positive expression rate, a strong proliferative response and the persistence of CAR-T cells in vivo. Manufacturing CAR-T cells is a process usually associated with the decreased CAR-positive expression rate and terminal differentiation of the infused CAR-T cells, which causes decreased proliferation and persistence of CAR-T cells in vivo. Therefore, the preparation of a high CAR-positive expression rate and few differentiated CAR-T cells is particularly important for clinical cancer treatment. In this study, we transduced and expanded CAR-T cells targeting the epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) in the presence of an Akt inhibitor (MK2206) during the initial stage of CAR-T cell preparation. We show that the Akt inhibitor did not suppress the proliferation or effector function of the EpCAM-CAR-T cells but increased the CAR-positive expression rate and decreased the number of terminally differentiated EpCAM-CAR-T cells. Furthermore, EpCAM-CAR-T cells prepared using this protocol appeared to have enhanced antitumor activity in vivo. Taken together, these findings suggest that Akt inhibition during the initial stage of CAR-T cell preparation could improve the performance of CAR-T cells.
Keywords: Akt inhibitor; CAR-T; CAR-positive expression rate; MK2206; memory phenotype.
AJCR Copyright © 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



References
-
- Zhang Q, Li H, Yang J, Li L, Zhang B, Li J, Zheng J. Strategies to improve the clinical performance of chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells for cancer. Curr Gene Ther. 2013;13:65–70. - PubMed
-
- Xu J, Tian K, Zhang H, Li L, Liu H, Liu J, Zhang Q, Zheng J. Chimeric antigen receptor-T cell therapy for solid tumors require new clinical regimens. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2017;17:1099–1106. - PubMed
-
- Wang XP, Lewis DE. CD86 expression correlates with amounts of HIV produced by macrophages in vitro. J Leukoc Biol. 2001;69:405–413. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
