15 years of the model study course in medicine at the Ruhr University Bochum
- PMID: 31815169
- PMCID: PMC6883250
- DOI: 10.3205/zma001267
15 years of the model study course in medicine at the Ruhr University Bochum
Abstract
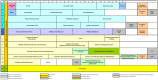
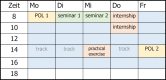
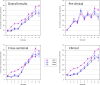
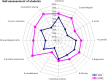
The Faculty of Medicine of the Ruhr University Bochum (RUB) introduced a model study course in medicine (MSM) in the winter semester 2003. For 9 consecutive years, 42 out of 280 first year students at the Ruhr University Bochum had the opportunity to begin their studies in the model study course in medicine. The places were allocated amongst the applicants internally through a raffle. The MSM was consistently problem-, practice- and patient-oriented and largely did away with lectures, broke with the distinction between a pre-clinical and clinical phase and tested basic knowledge in equivalent integrated exams focusing on clinical application. Following a comparative evaluation of the standard degree course (RSM) and the MSM, the faculty merged the two degree courses into the Integrated Reformed Medical Curriculum (IRMC), which has been on offer since 2013 and is characterized by a topic-oriented hybrid curriculum. This article examines experiences relating to the origins, conception and introduction of the MSM.
Zum Wintersemester 2003 führte die Medizinische Fakultät der Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) den Modellstudiengang Medizin (MSM) ein. Für 9 aufeinanderfolgende Jahrgänge hatten je 42 von 280 StudienanfängerInnen der Ruhr-Universität Bochum die Gelegenheit, ihr Studium im Modellstudiengang Medizin zu beginnen. Die Plätze wurden unter freiwilligen Bewerbungen intern verlost. Der konsequent Problem-, Praxis- und Patientenorientierte MSM verzichtete weitgehend auf Vorlesungen, hob die Trennung von Vorklinik und Klinik auf und prüfte die Grundlagenkenntnisse in äquivalenten, integrierten Prüfungen mit klinischen Anwendungen. Nach vergleichender Auswertung von Regelstudiengang (RSM) und MSM führte die Fakultät die beiden Studiengänge zu dem seit 2013 angebotenen integrierten Reformstudiengang Medizin (iRM) zusammen, der durch ein themenorientiertes Hybridcurriculum gekennzeichnet ist. Dieser Artikel befasst sich mit den Erfahrungen mit der Entstehung, Konzeption und Einführung des Modellstudiengangs Medizin.
Keywords: PBL; integration; problem-based learning; small group teaching; theme-oriented curriculum.
Copyright © 2019 Burger et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Knowles MS. The modern practice of adult education: From pedagogy to andragogy. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Cambridge Adult Education; 1980.
-
- Cooperstein SE, Kocevar-Weidinger E. Beyond active learning: A constructivist approach to learning. Ref Serv Rev. 2004;32(2):141–148. doi: 10.1108/00907320410537658. - DOI
-
- Schäfer T, Köster U, Huenges B, Burger A, Rusche H. Systematische Planung fächerübergreifenden Unterrichts am Beispiel des Modellstudiengangs Medizin an der Ruhr-Universität Bochum. GMS Z Med Ausbild. 2007;24(3):Doc147. Available from: https://www.egms.de/static/de/journals/zma/2007-24/zma000441.shtml.
-
- Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Der Rektor. Studienordnung der Ruhr-Universität Bochum für den Modellstudiengang Medizin. Bochum: Ruhr-Universität Bochum; 2005.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

