Machine learning can accurately predict pre-admission baseline hemoglobin and creatinine in intensive care patients
- PMID: 31815192
- PMCID: PMC6884624
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-019-0192-z
Machine learning can accurately predict pre-admission baseline hemoglobin and creatinine in intensive care patients
Abstract
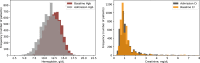
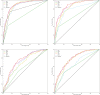
Patients admitted to the intensive care unit frequently have anemia and impaired renal function, but often lack historical blood results to contextualize the acuteness of these findings. Using data available within two hours of ICU admission, we developed machine learning models that accurately (AUC 0.86-0.89) classify an individual patient's baseline hemoglobin and creatinine levels. Compared to assuming the baseline to be the same as the admission lab value, machine learning performed significantly better at classifying acute kidney injury regardless of initial creatinine value, and significantly better at predicting baseline hemoglobin value in patients with admission hemoglobin of <10 g/dl.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Anaemia; Chronic kidney disease; Computational models; Data integration.
© The Author(s) 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Deyo D, Khaliq A, Mitchell D, Hughes DR. Electronic sharing of diagnostic information and patient outcomes. Am. J. Manag Care. 2018;24:32–37. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Haemoglobin concentrations for the diagnosis of anaemia and assessment of severity (2011).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

