In Vitro and in Vivo Studies of pH-Sensitive GHK-Cu-Incorporated Polyaspartic and Polyacrylic Acid Superabsorbent Polymer
- PMID: 31815212
- PMCID: PMC6893953
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.9b00655
In Vitro and in Vivo Studies of pH-Sensitive GHK-Cu-Incorporated Polyaspartic and Polyacrylic Acid Superabsorbent Polymer
Abstract
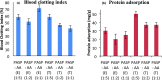
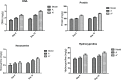
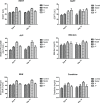
The main aim of this study was to evaluate the in vitro and in vivo efficiency of the polyaspartic acid- and acrylic acid-based superabsorbent polymer. The synthesized polymer was first investigated to check the blood compatibility by protein adsorption and blood clotting tests. Further, the GHK-Cu peptide was incorporated within the polymer and release studies were performed to evaluate the drug-delivery efficiency of the superabsorbent polymer. The polymer with best peptide release results were further used for in vivo analysis for wound healing. The healing efficiency of polymer with and without peptide was analyzed using wound closure, biochemical assay, histopathological, and toxicity studies.
Copyright © 2019 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): The financial funding was provided by University of Grant Commision, New Delhi, India (Grant No: F.No. 42-255/2013 (SR)).
Figures






References
-
- Sharma S.; Dua A.; Malik A. Third generation materials for wound dressings. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2014, 5, 2113–2124.
-
- Singh S.; Young A.; McNaught C. E. The physiology of wound healing. Surgery 2017, 35, 473–477. 10.1016/j.mpsur.2017.06.004. - DOI
-
- Johnson C. Management of Burns. Surgery 2018, 36, 435–440. 10.1016/j.mpsur.2018.05.004. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

