Intermediate-High Risk Pulmonary Embolism
- PMID: 31815247
- PMCID: PMC6892655
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0039-3401003
Intermediate-High Risk Pulmonary Embolism
Abstract
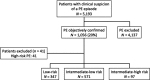
Limited information exists about the prevalence, management, and outcomes of intermediate-high risk patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). In a prospective cohort study, we evaluated consecutive patients with intermediate-high risk PE at a large, tertiary, academic medical center between January 1, 2015 and March 31, 2019. Adjudicated outcomes included PE-related mortality and a complicated course through 30 days after initiation of PE treatment. Repeat systolic blood pressure (SBP), heart rate (HR), brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), and cardiac troponin I (cTnI) measurements, and echocardiography were performed within 48 hours after diagnosis. Among 1,015 normotensive patients with acute PE, 97 (9.6%) had intermediate-high risk PE. A 30-day complicated course and 30-day PE-related mortality occurred in 23 (24%) and 7 patients (7.2%) with intermediate-high risk PE. Seventeen (18%) intermediate-high risk patients received reperfusion therapy. Within 48 hours after initiation of anticoagulation, normalization of SBP, HR, cTnI, BNP, and echocardiography occurred in 82, 86, 78, 72, and 33% of survivors with intermediate-high risk PE who did not receive immediate thrombolysis. A complicated course between day 2 and day 30 after PE diagnosis for the patients who normalized SBP, HR, cTnI, BNP, and echocardiography measured at 48 hours occurred in 2.9, 1.4, 4.5, 3.3, and 14.3%, respectively. Intermediate-high risk PE occurs in approximately one-tenth of patients with acute symptomatic PE, and is associated with high morbidity and mortality. Normalization of HR 48 hours after diagnosis might identify a group of patients with a very low risk of deterioration during the first month of follow-up.
Keywords: intermediate-high risk; prognosis; pulmonary embolism; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Kucher N, Rossi E, De Rosa M, Goldhaber S Z. Massive pulmonary embolism. Circulation. 2006;113(04):577–582. - PubMed
-
- Goldhaber S Z, Visani L, De Rosa M.Acute pulmonary embolism: clinical outcomes in the International Cooperative Pulmonary Embolism Registry (ICOPER) Lancet 1999353(9162):1386–1389. - PubMed
-
- Jiménez D, Bikdeli B, Barrios D et al.Epidemiology, patterns of care and mortality for patients with hemodynamically unstable acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. Int J Cardiol. 2018;269:327–333. - PubMed
-
- Konstantinides S V, Torbicki A, Agnelli Get al.2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism Eur Heart J 201435433033–3069., 3069a–3069k - PubMed
-
- Jiménez D, Aujesky D, Moores L et al.Combinations of prognostic tools for identification of high-risk normotensive patients with acute symptomatic pulmonary embolism. Thorax. 2011;66(01):75–81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials