Aqueous Partition of Methanolic Extract of Dicranopteris linearis Leaves Protects against Liver Damage Induced by Paracetamol
- PMID: 31817058
- PMCID: PMC6950669
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11122945
Aqueous Partition of Methanolic Extract of Dicranopteris linearis Leaves Protects against Liver Damage Induced by Paracetamol
Abstract
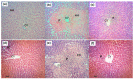
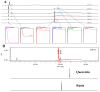
This study aimed to determine the antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities of semi-purified aqueous partition obtained from the methanol extract of Dicranopteris linearis (AQDL) leaves against paracetamol (PCM)-induced liver intoxication in rats. The test solutions, AQDL (50, 250, and 500 mg/kg), were administered orally to rats (n = 6) once daily for seven consecutive days followed by the hepatotoxicity induction using 3 g/kg PCM (p.o.). Blood was collected for serum biochemical parameters analysis while the liver was collected for histopathological examination and endogenous antioxidant enzymes analysis. AQDL was also subjected to antioxidant determination and phytochemical analysis. Results obtained show that AQDL possessed high total phenolic content (TPC) value and remarkable radical scavenging activities. AQDL also significantly (p < 0.05) reduced the liver weight/body weight (LW/BW) ratio or serum level of ALT, AST, and total bilirubin while significantly (p < 0.05) increase the level of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) without affecting the malondialdehyde (MDA) in the liver indicating its hepatoprotective effect. Phytoconstituents analyses showed only the presence of saponins and triterpenes, but lack of flavonoids. In conclusion, AQDL exerts hepatoprotective activity via its high antioxidant potential and ability to modulate the endogenous enzymatic antioxidant defense system possibly via the synergistic action of saponins and triterpenes.
Keywords: Dicranopteris linearis; endogenous antioxidant enzymes; free radical scavenging activity; hepatoprotective; phenolic derivatives; saponins; triterpenes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The sponsors had no role in the design, execution, interpretation, or writing of the study.
Figures
References
-
- Heard K., Green J.L., Bailey J.E., Bogdan G.M., Dart R.C. A randomized trial to determine the change in alanine aminotransferase during 10 days of paracetamol (acetaminophen) administration in subjects who consume moderate amounts of alcohol. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007;26:283–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2007.03368.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

