The therapeutic potential of targeting tryptophan catabolism in cancer
- PMID: 31819194
- PMCID: PMC6964670
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-019-0664-6
The therapeutic potential of targeting tryptophan catabolism in cancer
Abstract
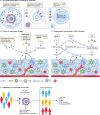
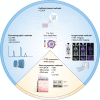
Based on its effects on both tumour cell intrinsic malignant properties as well as anti-tumour immune responses, tryptophan catabolism has emerged as an important metabolic regulator of cancer progression. Three enzymes, indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase 1 and 2 (IDO1/2) and tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase (TDO2), catalyse the first step of the degradation of the essential amino acid tryptophan (Trp) to kynurenine (Kyn). The notion of inhibiting IDO1 using small-molecule inhibitors elicited high hopes of a positive impact in the field of immuno-oncology, by restoring anti-tumour immune responses and synergising with other immunotherapies such as immune checkpoint inhibition. However, clinical trials with IDO1 inhibitors have yielded disappointing results, hence raising many questions. This review will discuss strategies to target Trp-degrading enzymes and possible down-stream consequences of their inhibition. We aim to provide comprehensive background information on Trp catabolic enzymes as targets in immuno-oncology and their current state of development. Details of the clinical trials with IDO1 inhibitors, including patient stratification, possible effects of the inhibitors themselves, effects of pre-treatments and the therapies the inhibitors were combined with, are discussed and mechanisms proposed that might have compensated for IDO1 inhibition. Finally, alternative approaches are suggested to circumvent these problems.
Conflict of interest statement
C.A.O. and M.P. are listed as inventors on the patents “Means and methods for treating and/or preventing natural AHR ligand-dependent cancer” and “Isotopic method for measurement of tryptophan and metabolites thereof”. M.P. is listed on the patent “Treatment of Kynurenine-producing tumors with AHR antagonists”. M.P. has received research support and consulting honoraria from Bayer. The other authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Platten M, Nollen EAA, Rohrig UF, Fallarino F, Opitz CA. Tryptophan metabolism as a common therapeutic target in cancer, neurodegeneration and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019;18:379–401. - PubMed
-
- Brenk M, Scheler M, Koch S, Neumann J, Takikawa O, Hacker G, et al. Tryptophan deprivation induces inhibitory receptors ILT3 and ILT4 on dendritic cells favoring the induction of human CD4+CD25+ Foxp3+ T regulatory cells. J. Immunol. 2009;183:145–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No 754688/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)/International
- No 643638/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)/International
- No 754688/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)/International
- 01ZX1402/Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (Federal Ministry of Education and Research)/International
- 01ZX1402/Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (Federal Ministry of Education and Research)/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

