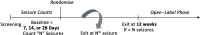Novel study design to assess the efficacy and tolerability of antiseizure medications for focal-onset seizures in infants and young children: A consensus document from the regulatory task force and the pediatric commission of the International League against Epilepsy (ILAE), in collaboration with the Pediatric Epilepsy Research Consortium (PERC)
- PMID: 31819909
- PMCID: PMC6885693
- DOI: 10.1002/epi4.12356
Novel study design to assess the efficacy and tolerability of antiseizure medications for focal-onset seizures in infants and young children: A consensus document from the regulatory task force and the pediatric commission of the International League against Epilepsy (ILAE), in collaboration with the Pediatric Epilepsy Research Consortium (PERC)
Abstract
High-quality placebo-controlled drug trials for focal-onset seizures in infants and children younger than 4 years have become increasingly difficult to perform because of eligibility constraints and onerous study designs. Traditional designs used in these populations require a high baseline seizure frequency, two hospitalizations for video-electroencephalography (video-EEG) monitoring, and willingness to accept potential exposure to placebo when the drugs to be tested are usually already available for off-label prescription. To address these constraints, the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) regulatory taskforce and the ILAE pediatric commission, in collaboration with the Pediatric Epilepsy Research Consortium (PERC), propose a novel trial design which involves seizure counting by caregivers based on previous video-EEG/video validation of specific seizure semiologies. We present a novel randomized placebo-controlled trial design intended to be used for studying new antiseizure medications (ASMs) for focal-onset seizures (FOS) in children aged one month to four years. This design uses "time to Nth seizure" as the primary outcome and incorporates a new element of variable baseline duration. This approach permits enrollment of infants with lower seizure burden, who might not have video-EEG-recorded seizures within 2-3 days of monitoring. Repeated hospitalizations for video-EEG recordings are avoided, and duration of baseline and exposure to placebo or ineffective treatment(s) are minimized. By broadening eligibility criteria, reducing risks from prolonged placebo exposure, and relying on validated recording of seizure counting by caregivers, clinical trials will be likely to be completed more efficiently than in the recent past.
Keywords: antiseizure drugs; children; clinical trials; drug development; infants.
© 2019 The Authors. Epilepsia Open published by Wiley Periodicals Inc. on behalf of International League Against Epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
S Auvin receives salary support from Université de Paris and Assistance Publique—Hôpitaux de Paris. Stéphane Auvin is Associate Editor for Epilepsia. He is an investigator on research grants awarded to Robert‐Debré University Hospital from Advicenne Pharma, EISAI, UCB Zogenix; he has received travel expenses or consulting fee from Arvelle, Advicenne Pharma, Biocodex, Biomarin, Eisai, GW Pharma, Novartis, Nutricia, Shire, UCB Pharma, Vitaflo, Zogenix. J. French receives NYU salary support from the Epilepsy Foundation and for consulting work and/or attending Scientific Advisory Boards on behalf of the Epilepsy Study Consortium for Acadia, Adamas, Addex, Aeonian, Alexza, Anavex, Arvelle Therapeutics, Inc, Axcella Health, Axovant, Biogen, Biomotiv/Koutif, Blackfynn, Bloom Science, Bridge Valley Ventures, Cavion, Cerebral Therapeutics, Cerevel, Clinilabs, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Covance, Crossject, CuroNZ, Eisai, Empatica, Encoded, Engage Therapeutics, Epitel, GW Pharma, Idorsia, Impax, Ionis, J&J Pharmaceuticals, Marinus, MonosolRx, Neurelis, Neurocrine, Novartis, Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development, Ovid Therapeutics Inc, Pfizer, Pfizer‐Neusentis, Praxis, Redpin, Sage, Sancillio, Shire, SK Life Sciences, Springworks, Stoke, Sunovion, Supernus, Takeda, UCB Inc, Ultragenyx, Upsher Smith, Vyera, West Therapeutic Development, Xenon, Xeris, Zogenix, Zynerba.J. French has also received research grants from Biogen, Cavion, Eisai, Engage, GW Pharma, Lundbeck, Neurelis, Ovid, SK Life Sciences, Sunovion, UCB, and Zogenix as well as grants from the Epilepsy Research Foundation, Epilepsy Study Consortium, and NINDS. She is on the editorial board of Lancet Neurology and Neurology Today. She is scientific officer for the Epilepsy Foundation for which NYU receives salary support. She has received travel reimbursement related to research, advisory meetings, or presentation of results at scientific meetings from the Epilepsy Study Consortium, the Epilepsy Foundation, Adamas, Arvelle Therapeutics, Inc, Axovant, Biogen, Blackfynn, Crossject, CuroNz, Eisai, Engage, Idorsia, Neurelis, Novartis, Otsuka, Ovid, Pfizer, Redpin, Sage, SK Life Science, Sunovion, Takeda, UCB, Ultragenyx, Zynerba. Dr Dlugos receives salary support from NIH, Commonwealth of Pennsylvania Department of Health, Pediatric Epilepsy Research Foundation, and The Epilepsy Study Consortium; he is an investigator on research grants awarded to CHOP from Zogenix, Greenwich Biosciences, UCB, Brain Sentinel, Neurelis, Pfizer, Q‐State, USL, Aquestive, Sage, Bio‐Pharm, Insys, SK Life Sciences, Biogen, and Encoded Therapeutics; he has received travel expenses for protocol development or investigator meetings from Marinus, Ovid/Takeda, Ultragenyx, USL, Pfizer, and Zogenix. Dr Knupp receives research support from West pharmaceuticals, Zogenix, and the Pediatric Epilepsy Research Foundation. She has received consulting funds from Zogenix and Greenwich Biosciences. Dr Perucca received speakers/consultancy fees from Amicus Pharma, Arvelle, Biogen, Eisai, GW Pharma, Sanofi, Sun Pharma, Takeda, UCB Pharma, and Xenon Pharma. His contribution to this work was partly supported by a European Union grant to the EpiCARE European Reference Network. Dr Arzimanoglou receives salary support from the University Hospitals of Lyon (HCL). His work is also partly supported by the European Union grant to the EpiCARE European Reference Network. He has a mission of Editor‐in‐Chief for the ILAE educational journal Epileptic Disorders and of Associate Editor for the European Journal of Paediatric Neurology. He is an investigator on research grants awarded to HCL, France and Sant Joan de Déu Hospital Barcelona from the Caixa Foundation and UCB; he has received travel expenses or consulting fees from Advicenne Pharma, Biomarin, Eisai, GW Pharma, Shire, UCB Pharma, Zogenix. Ed Whalen, PhD, is a full‐time employee of Pfizer Inc He holds Pfizer stock and receives stock as part of his compensation. Dr Shellhaas receives research support from PCORI, NIH, and the Pediatric Epilepsy Research Foundation. She serves as a consultant to the Epilepsy Study Consortium and receives royalties from UpToDate for authorship of topics related to neonatal seizures. We confirm that we have read the Journal's position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
Figures
References
-
- Zarrelli MM, Beghi E, Rocca WA, Hauser WA. Incidence of epileptic syndromes in Rochester, Minnesota: 1980–1984. Epilepsia. 1999;40(12):1708–14. - PubMed
-
- Franco V, Canevini MP, Capovilla G, De Sarro G, Galimberti CA, Gatti G, et al. Off‐label prescribing of antiepileptic drugs in pharmacoresistant epilepsy: a cross‐sectional drug utilization study of tertiary care centers in Italy. CNS Drugs. 2014;28(10):939–49. - PubMed
-
- Kuchenbuch M, Chemaly N, Henniene K, Kaminska A, Chiron C, Nabbout R. Off‐label use and manipulations of antiepileptic drugs in children: analysis of the outpatient prescriptions in a tertiary center. Epilepsy Behav. 2018;82:133–9. - PubMed
-
- https://www.fda.gov/drugs/development-resources/pediatric-research-equit.... Accessed May 18, 2019.
-
- European Union ‐ Drug development . https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/health/files/files/eudralex/vol-1/dir_.... Accessed May 18, 2019.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous