Using Reverse Phase Protein Array (RPPA) to Identify and Target Adaptive Resistance
- PMID: 31820393
- PMCID: PMC7382818
- DOI: 10.1007/978-981-32-9755-5_14
Using Reverse Phase Protein Array (RPPA) to Identify and Target Adaptive Resistance
Abstract
Tumor cells and the tumor ecosystem rapidly evolve in response to therapy. This tumor evolution results in the rapid emergence of drug resistance that limits the magnitude and duration of response to therapy including chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Thus, there is an urgent need to understand and interdict tumor evolution to improve patient benefit to therapy. Reverse phase protein array (RPPA) provides a powerful tool to evaluate and develop approaches to target the processes underlying one form of tumor evolution: adaptive evolution. Tumor cells and the tumor microenvironment rapidly evolve through rewiring of protein networks to bypass the effects of therapy. In this review, we present the concepts underlying adaptive resistance and use of RPPA in understanding resistance mechanisms and identification of effective drug combinations. We further demonstrate that this novel information is resulting in biomarker-driven trials aimed at targeting adaptive resistance and improving patient outcomes.
Keywords: Adaptive resistance; Combination therapy; Reverse phase protein array; Targeted therapy; Tumor evolution.
Figures
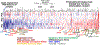
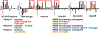
References
-
- Akbani R, Ng PK, Werner HM, Shahmoradgoli M, Zhang F, Ju Z, Liu W, Yang JY, Yoshihara K, Li J, Ling S, Seviour EG, Ram PT, Minna JD, Diao L, Tong P, Heymach JV, Hill SM, Dondelinger F, Stadler N, Byers LA, Meric-Bernstam F, Weinstein JN, Broom BM, Verhaak RG, Liang H, Mukherjee S, Lu Y, Mills GB (2014) A pan-cancer proteomic perspective on The Cancer Genome Atlas. Nat Commun 5:3887. doi:10.1038/ncomms4887 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Budina-Kolomets A, Webster MR, Leu JI, Jennis M, Krepler C, Guerrini A, Kossenkov AV, Xu W, Karakousis G, Schuchter L, Amaravadi RK, Wu H, Yin X, Liu Q, Lu Y, Mills GB, Xu X, George DL, Weeraratna AT, Murphy ME (2016) HSP70 Inhibition Limits FAK-Dependent Invasion and Enhances the Response to Melanoma Treatment with BRAF Inhibitors. Cancer Res 76 (9):2720–2730. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2137 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Echevarria-Vargas IM, Reyes-Uribe PI, Guterres AN, Yin X, Kossenkov AV, Liu Q, Zhang G, Krepler C, Cheng C, Wei Z, Somasundaram R, Karakousis G, Xu W, Morrissette JJ, Lu Y, Mills GB, Sullivan RJ, Benchun M, Frederick DT, Boland G, Flaherty KT, Weeraratna AT, Herlyn M, Amaravadi R, Schuchter LM, Burd CE, Aplin AE, Xu X, Villanueva J (2018) Co-targeting BET and MEK as salvage therapy for MAPK and checkpoint inhibitor-resistant melanoma. EMBO Mol Med 10 (5). doi:10.15252/emmm.201708446 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

