Recombinant FIX Fc fusion protein activity assessment with the one-stage clotting assay: A multicenter, assessor-blinded, prospective study in Japan (J-Field Study)
- PMID: 31820573
- PMCID: PMC7078902
- DOI: 10.1111/ijlh.13133
Recombinant FIX Fc fusion protein activity assessment with the one-stage clotting assay: A multicenter, assessor-blinded, prospective study in Japan (J-Field Study)
Abstract
Introduction: The one-stage clotting assay is used to measure factor IX (FIX) activity in patients' plasma samples and in FIX products for hemophilia treatment. However, the diversity of reagents and instruments has resulted in significant FIX assay variability.
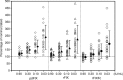
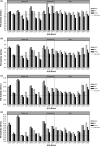
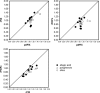
Methods: The accuracy of the one-stage clotting assay to measure recombinant FIX Fc fusion protein (rFIXFc) activity was evaluated by major Japanese hemophilia treatment centers and commercial laboratories that measure factor IX activity for a majority of hemophilia B patients in Japan. Plasma-derived FIX (pdFIX) and recombinant FIX (rFIX) products were used as comparators. FIX-deficient plasma was spiked with four levels of FIX products based on label potency and measured under blinded conditions by routine one-stage clotting assay procedures in 19 participating laboratories. Interlaboratory coefficient of variation and spike recovery were calculated.
Results: Interlaboratory coefficient of variation of rFIXFc was not significantly different from that of rFIX, but appeared larger than that of pdFIX. Mean spike recovery for rFIXFc was generally comparable to rFIX and pdFIX. However, larger discrepancies between pdFIX and rFIX were observed in three of nine laboratories using ellagic acid-based activated partial thromboplastin time reagents.
Conclusion: Recombinant FIX Fc fusion protein activity was found to be similar to that of rFIX or pdFIX by the one-stage clotting assay. However, minimizing interlaboratory variability is vital for optimizing future patient care.
Keywords: Japan; biological assay; factor IX; hemophilia B; recombinant FIX Fc fusion protein.
2019 Sanofi K.K. International Journal of Laboratory Hematology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Katsuyuki Fukutake has received grants from Baxalta, Bayer, Pfizer, CSL Behring, Novo Nordisk, Biogen, Kaketsuken, Japan Blood Products Organization, and Ortho Clinical Diagnostics; personal fees from Baxalta, Bayer, Pfizer, CSL Behring, Novo Nordisk, Biogen, Kaketsuken, SRL Inc, LSI Medience, Roche Diagnostics, Siemens, Sekisui Medical, Fujirebio Inc, Abbott, Torii Pharmaceuticals, Octapharma, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. LTD, and BioMarin; and other fees from CIMIC outside the submitted work. Tomomi Kobayashi is a current employee of Bioverativ Japan Ltd. Jurg M. Sommer is a former employee of and current consultant for Bioverativ, a Sanofi company. Toshiyuki Hirakata is a former employee of Biogen Japan Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Real-world assay variability between laboratories in monitoring of recombinant factor IX Fc fusion protein activity in plasma samples.Int J Lab Hematol. 2020 Jun;42(3):350-358. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.13189. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Int J Lab Hematol. 2020. PMID: 32202380 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of a recombinant fusion protein linking coagulation factor IX with recombinant albumin in one-stage clotting assays.J Thromb Haemost. 2019 Jan;17(1):138-148. doi: 10.1111/jth.14332. Epub 2018 Dec 16. J Thromb Haemost. 2019. PMID: 30418692 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative field study: impact of laboratory assay variability on the assessment of recombinant factor IX Fc fusion protein (rFIXFc) activity.Thromb Haemost. 2014 Nov;112(5):932-40. doi: 10.1160/TH13-11-0971. Epub 2014 Aug 21. Thromb Haemost. 2014. PMID: 25144892 Free PMC article.
-
Continuous prophylaxis with recombinant factor IX Fc fusion protein and conventional recombinant factor IX products: comparisons of efficacy and weekly factor consumption.J Med Econ. 2017 Apr;20(4):337-344. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2016.1265973. Epub 2016 Dec 21. J Med Econ. 2017. PMID: 27885871
-
Factor VIII and IX assays for post-infusion monitoring in hemophilia patients: Guidelines from the French BIMHO group (GFHT).Eur J Haematol. 2020 Aug;105(2):103-115. doi: 10.1111/ejh.13423. Epub 2020 May 27. Eur J Haematol. 2020. PMID: 32277501 Review.
Cited by
-
An Update on Laboratory Diagnostics in Haemophilia A and B.Hamostaseologie. 2022 Aug;42(4):248-260. doi: 10.1055/a-1665-6232. Epub 2022 Feb 1. Hamostaseologie. 2022. PMID: 35104901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-world assay variability between laboratories in monitoring of recombinant factor IX Fc fusion protein activity in plasma samples.Int J Lab Hematol. 2020 Jun;42(3):350-358. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.13189. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Int J Lab Hematol. 2020. PMID: 32202380 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Srivastava A, Brewer AK, Mauser‐Bunschoten EP, et al. Guidelines for the management of haemophilia. Haemophilia. 2013;19:e1‐e47. - PubMed
-
- Wilmot HV, Hogwood J, Gray E. Recombinant factor IX: discrepancies between one‐stage clotting and chromogenic assays. Haemophilia. 2014;20:891‐897. - PubMed
-
- Hubbard AR, Dodt J, Lee T, et al. Recommendations on the potency labelling of factor VIII and factor IX concentrates. J Thromb Haemost. 2013;11(5):988‐989. - PubMed
-
- Barrowcliffe TW. Insights from factor IX activation studies with chromogenic assays: implications of disparate product results. Haemophilia. 2010;16(Suppl 6):9‐12. - PubMed
-
- Pouplard C, Trossaert M, Le Querrec A, Delahousse B, Giraudeau B, Gruel Y. Influence of source of phospholipids for aPTT‐based factor IX assays and potential consequences for the diagnosis of mild hemophilia B. Haemophilia. 2009;15:365‐368. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

