Fetal fraction and noninvasive prenatal testing: What clinicians need to know
- PMID: 31821597
- PMCID: PMC10040212
- DOI: 10.1002/pd.5620
Fetal fraction and noninvasive prenatal testing: What clinicians need to know
Abstract
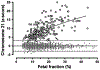
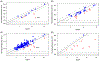
The fetal fraction (FF) is a function of both biological factors and bioinformatics algorithms used to interpret DNA sequencing results. It is an essential quality control component of noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPT) results. Clinicians need to understand the biological influences on FF to be able to provide optimal post-test counseling and clinical management. There are many different technologies available for the measurement of FF. Clinicians do not need to know the details behind the bioinformatics algorithms of FF measurements, but they do need to appreciate the significant variations between the different sequencing technologies used by different laboratories. There is no universal FF threshold that is applicable across all platforms and there have not been any differences demonstrated in NIPT performance by sequencing platform or method of FF calculation. Importantly, while FF should be routinely measured, there is not yet a consensus as to whether it should be routinely reported to the clinician. The clinician should know what to expect from a standard test report and whether reasons for failed NIPT results are revealed. Emerging solutions to the challenges of samples with low FF should reduce rates of failed NIPT in the future. In the meantime, having a "plan B" prepared for those patients for whom NIPT is unsuccessful is essential in today's clinical practice.
© 2019 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gahan PB, ed. Circulating nucleic acids in early diagnosis, prognosis and treatment monitoring: an introduction. Advances in predictive, preventive and personalised medicine. Vol 5. Netherlands: Springer Publishing; 2015. 10.1007/978-94-017-9168-7_11. - DOI
-
- Faas BH, de Ligt J, Janssen I, et al. Non-invasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal aneuploidies using massively parallel sequencing-by ligation and evidence that cell-free fetal DNA in the maternal plasma originates from cytotrophoblastic cells. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12: S19–S26. - PubMed
-
- Alberry M, Maddocks D, Jones M, et al. Free fetal DNA in maternal plasma in anembryonic pregnancies: confirmation that the origin is the trophoblast. Prenat Diagn. 2007;27:415–418. - PubMed
-
- Flori E, Doray B, Gautie E, et al. Circulating cell-free fetal DNA in maternal serum appears to originate from cyto- and syncytiotrophoblastic cells. Case report. Hum Reprod. 2004;19:723–724. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

