Activation of Distinct Channelrhodopsin Variants Engages Different Patterns of Network Activity
- PMID: 31822522
- PMCID: PMC6944482
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0222-18.2019
Activation of Distinct Channelrhodopsin Variants Engages Different Patterns of Network Activity
Abstract
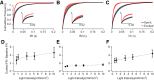
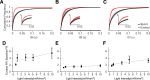
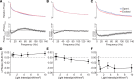
Several recently developed Channelrhodopsin (ChR) variants are characterized by rapid kinetics and reduced desensitization in comparison to the widely used ChR2. However, little is known about how varying opsin properties may regulate their interaction with local network dynamics. We compared evoked cortical activity in mice expressing three ChR variants with distinct temporal profiles under the CamKII promoter: Chronos, Chrimson, and ChR2. We assessed overall neural activation by measuring the amplitude and temporal progression of evoked spiking. Using γ-range (30-80 Hz) local field potential (LFP) power as an assay for local network engagement, we examined the recruitment of cortical network activity by each tool. All variants caused light-evoked increases in firing in vivo, but each demonstrated different temporal patterning of evoked activity. In addition, the three ChRs had distinct effects on cortical γ-band activity. Our findings suggest the properties of optogenetic tools can substantially affect their efficacy in vivo, as well their engagement of circuit resonance.
Keywords: Channelrhodopsin; Chrimson; Chronos; cortex; optogenetics; γ oscillations.
Copyright © 2020 Jun and Cardin.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
