A synopsis of recent developments defining how N-glycosylation impacts immunoglobulin G structure and function
- PMID: 31822882
- PMCID: PMC7109350
- DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cwz068
A synopsis of recent developments defining how N-glycosylation impacts immunoglobulin G structure and function
Abstract
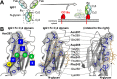
Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are the fastest growing group of drugs with 11 new antibodies or antibody-drug conjugates approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2018. Many mAbs require effector function for efficacy, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity triggered following contact of an immunoglobulin G (IgG)-coated particle with activating crystallizable fragment (Fc) γ receptors (FcγRs) expressed by leukocytes. Interactions between IgG1 and the FcγRs require post-translational modification of the Fc with an asparagine-linked carbohydrate (N-glycan). Though the structure of IgG1 Fc and the role of Fc N-glycan composition on disease were known for decades, the underlying mechanism of how the N-glycan affected FcγR binding was not defined until recently. This review will describe the current understanding of how N-glycosylation impacts the structure and function of the IgG1 Fc and describe new techniques that are poised to provide the next critical breakthroughs.
Keywords: Fc gamma receptor; N-glycosylation; antibody; immunoglobulin G.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures