Is there an optimal conditioning for older patients with AML receiving allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation?
- PMID: 31826244
- PMCID: PMC8212356
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2019003662
Is there an optimal conditioning for older patients with AML receiving allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation?
Abstract
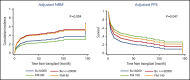
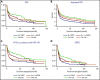
The optimal conditioning regimen for older patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) remains unclear. In this study, we compared outcomes of AML patients >60 years of age undergoing allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation at our institution. All 404 consecutively treated patients received 1 of the following conditioning regimens: (1) fludarabine+melphalan 100 mg/m2 (FM100), (2) fludarabine+melphalan 140 mg/m2 (FM140), (3) fludarabine+IV busulfan AUC ≥ 5000/d × 4 d (Bu≥20000), and (4) fludarabine+IV busulfan AUC 4000/d × 4 d (Bu16000). A propensity score analysis (PSA) was used to compare outcomes between these 4 groups. Among the 4 conditioning regimens, the FM100 group had a significantly better long-term survival with 5-year progression-free survival of 49% vs 30%, 34%, and 23%, respectively. The benefit of the FM100 regimen resulted primarily from the lower nonrelapse mortality associated with this regimen, an effect more pronounced in patients with lower performance status. The PSA confirmed that FM100 was associated with better posttransplantation survival, whereas no significant differences were seen between the other regimen groups. In summary, older patients with AML benefited from a reduced-intensity conditioning regimen with lower melphalan doses (FM100), which was associated with better survival, even though it was primarily used in patients who could not receive a more intense conditioning regimen.
© 2020 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Giralt S, Thall PF, Khouri I, et al. . Melphalan and purine analog-containing preparative regimens: reduced-intensity conditioning for patients with hematologic malignancies undergoing allogeneic progenitor cell transplantation. Blood. 2001;97(3):631-637. - PubMed
-
- Slavin S, Nagler A, Naparstek E, et al. . Nonmyeloablative stem cell transplantation and cell therapy as an alternative to conventional bone marrow transplantation with lethal cytoreduction for the treatment of malignant and nonmalignant hematologic diseases. Blood. 1998;91(3):756-763. - PubMed
-
- Ciurea SO, Rodrigues M, Giralt S, de Lima M. Aging, acute myelogenous leukemia, and allogeneic transplantation: do they belong in the same sentence? Clin Lymphoma Myeloma. 2009;9(4):289-297. - PubMed
-
- Devine SM, Owzar K, Blum W, et al. . Phase II Study of Allogeneic Transplantation for Older Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia in First Complete Remission Using a Reduced-Intensity Conditioning Regimen: Results From Cancer and Leukemia Group B 100103 (Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology)/Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trial Network 0502. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(35):4167-4175. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous